

Phishing
The danger of malicious phishing mails
In this article, you’ll learn what phishing is, how it works, and how to recognize the warning signs of a phishing attempt. We’ll explore different types of phishing — like spear phishing, smishing, and quishing — and offer practical advice on how to protect yourself and your organization through awareness, authentication protocols, and advanced email security solutions.
What is phishing?
Phishing is a type of social engineering, which mostly works via scam emails. It’s a way hackers try to manipulate victims to lead them to a specific reaction, like typing in a password or opening a malicious document. The cyber-criminals try to bypass the email security companies have via appealing to specific employees in a personal way. Phishing is not malware, it’s a scam tactic, that elite hackers have in their toolbox to gain information or spread malware in order to breach the security of companies without an extended amount of effort. How exactly does this technique work? How can you protect yourself?
The basic knowledge of phishing
First, you should know what Social Engineering is. Social Engineering is in general, applied social sciences, but better known as social manipulation or scamming. For Social Engineering the offender uses psychological knowledge to manipulate the victim to do what they want them to do. One technique is to pretend to be a colleague of the victim, an example would be a colleague from the system administration department sending out a scam email disguised as email from system administration department head. The victim is a way more willing to do, what the hacker wants the victim to do with his computer if he thinks that the attacker is a colleague. Another method is to prepare a scam email, which looks like an email from a company you trust, like PayPal. The hacker uses this scam email to lead the victim into the trap to gain access to their PayPal account.
Phishing is a scam email attack from cyber-criminals using the techniques discussed above. In general, there are two types of phishing attacks. First the easier method, the cyber-criminal doesn’t need much information about the victim. He sends out as many phishing emails as possible, to as many recipients as possible. Underlining the idea, that in a mass of people, someone will react in the way they want them to react. The chance getting higher and higher the more emails sent out. The other variation of phishing emails is called spear phishing. Spear phishing emails are much more personalized than a normal phishing email. The hacker tries to attack one particular victim and manipulates them with emails to give over the data wanted. One variation of this based on a two-step approach is called Barrel Phishing.
How does Phishing work?
Normally the target of the cyber-criminal, also known as a Phisher, is able to get login credentials, mostly of services like PayPal or similar. Otherwise, they are usually attempting to steal credit card information. In order to reach this goal, they use phishing emails. These emails are often structured like an email from the real service (Paypal, etc), which the hackers use to trick the user into giving up their login credentials. For example, they build an email that looks like an email from PayPal. In this email you are often asked to click on a link to type in a new password, because someone new logged in to your account or something similar. They can also use attached documents, in which case you are asked to open the file mimicing something like an invoice, with Malware inside. This malware could be tracking everything you do on your computer afterwards. It could sound a little bit paradox that phishing emails work with emails, that normally should warn you about someone trying to get into your account.
That is the moment the social engineering part of it is important. In the moment you get an email, that says someone tried to get in your account, you get in psychological stress. Imagine someone successfully stole your PayPal credentials, they could have potential access to all of your money. The hackers are using these thoughts to manipulate their victims.
Types of Phishing Attacks
Spear phishing or business email compromise (BEC)
A highly targeted form of phishing, spear phishing impersonates individuals rather than businesses. Most often, the spoofed individual is someone known by the victim. Spear phishing attacks also don’t contain malicious links or attachments, making them seem harmless even to a cautious recipient.
The cyber-criminal upfront tries to get as much information as possible about his victim. In this instance there is a lot of research done before being able to execute this phishing attack. The hacker has to spy out his victim. They do not send out a mass of phishing emails, they are only interested in one target. Most of the time, this is a specific company head or executive. The more personal information they have about their victim, the better they can attack.
Spear phishing attacks are often financially motivated, with hackers seeking a quick payout. In most cases, attackers use publicly available information (such as company websites and social media profiles) to craft highly convincing messages that appear credible at first glance.
Quishing
Also known as QRishing or QR code phishing, quishing hides malicious links or attachments in QR codes to bypass detection by email filters. Beyond the techniques used to evade detection, quishing attacks attempt to achieve the same outcome as standard email phishing threats.
Whaling
Whaling is a type of spear phishing that targets senior executives, often to facilitate a financial scam such as wire transfer fraud. Whaling attacks rely on the same social engineering techniques as spear phishing attacks. The difference is largely the individual targeted, rather than how it occurs. According to the National Cyber Security Centre (NCSC), whaling attacks primarily focus on financial institutions and payment services, while cloud storage sites, online services, and e-commerce organizations can also be commonly affected.
Clone phishing
In this attack, hackers clone a legitimate email and modify it by substituting benign links and attachments with malicious ones. They then resend the email to the original recipient with the assumption that the intended victim is more likely to trust the content and sender based on their past experiences.
Social media phishing
Social media phishing is one of the most common types of email phishing. It impersonates social media brands and targets users with fake notifications, alerts, and other messages. Often, emails direct users to malicious websites designed to steal their credentials and use them to login to their social media accounts.
If hackers are successful in compromising an account, they can surveil their victims, facilitate an account takeover (ATO), as well as impersonate the victim and target friends, family, and other connections. Since 2020, Facebook has remained the top #1 or #2 most impersonated brand by hackers. Other brands, such as Instagram and WhatsApp, commonly feature among the most impersonated brands.
Vishing or voice phishing
Vishing occurs primarily or strictly through voice communication. Vishing attacks attempt to manipulate the intended victim into divulging sensitive information over the phone. This attack method can incorporate other channels of communication such as email or occur entirely over the phone. According to CISA, advanced vishing attacks often leverage Voice over Internet Protocol (VoIP) solutions so hackers can spoof legitimate callers.
Smishing or SMS phishing. Smishing, or SMS (short message service) phishing, occurs via text message. Like email phishing, smishing impersonates a known and established brand and sends the intended victim a text message containing a malicious link, request for information, or phone number controlled by the hacker for a vishing attempt. The aim of smishing is the same as email phishing.
Angler phishing
Angler phishing takes place on social media platforms. Hackers create fake profiles and pose as customer service representatives. They then target individuals on the platform that have posted complaints about the brand. As a fake gesture of goodwill, hackers may offer a refund, free giveaway, or another enticing offer that directs the targeted user to a malicious and illegitimate site.
Search engine phishing
Also known as search engine optimization (SEO) poisoning, search engine phishing is when hackers use SEO techniques to rank a malicious site in the top results for a search term. Designed to appear legitimate, the site is intended to harvest credentials or infect devices.
Email phishing
Email phishing is the most common type of phishing. It occurs when hackers impersonate a well-known brand and send an email containing malicious links or attachments to an intended victim. These attacks use social engineering techniques to entice the recipient to click a phishing link or download a harmful attachment. Hackers may use email phishing to harvest a victim’s credentials, infect a device with malware, carry out a subsequent cyberattack, and more.
How can I detect phishing?
How can you differentiate between the real email? Which is very important to get, and those emails which are just phishing emails? There are a few warning signs which help to recognize phishing emails, and differentiate them to the real emails. With these simple tricks you often can identify phishing emails. It is important to train yourself to question every email, especially those you didn’t expect, with the question “could this be a phishing email?”
Missing personal salutation
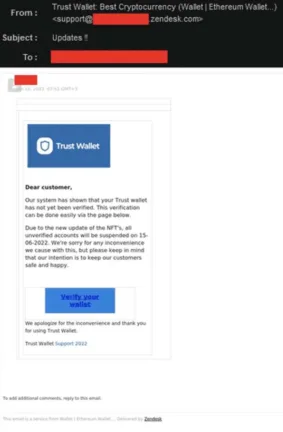
First thing you can look for is, if the email is addressing you with your name. Often phishing emails using phrases like “dear customer” or similar. The real companies often use your name, to make sure you can see their email isn’t a phishing email and it sounds a way more serious.
The sender
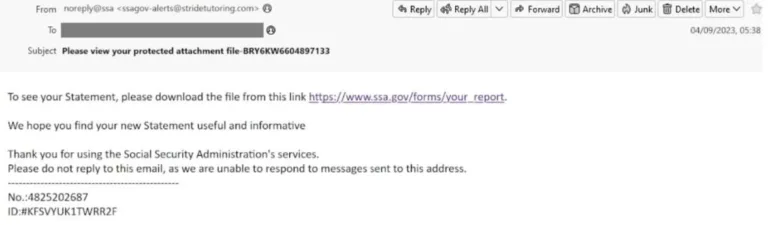
To protect yourself from a phishing email, double check the email address. Often the email address is very similar to the standard email address from the real company, but is not the proper sender address. For example, the real email address would be service@paypal.com and the phishing email address could be service@paypai.com. Within the first look you wouldn’t see a difference. So, you have to train yourself to take a closer look at the sender of emails, to make ensure that it is not a phishing email.
Email header
On the other hand, good cyber-criminals are able to manipulate the email in a way that it looks like you got the email from the sender you expected. For people with a strong technical background there is the opportunity to investigate the email header to find code that shouldn’t be there or is incorrect.
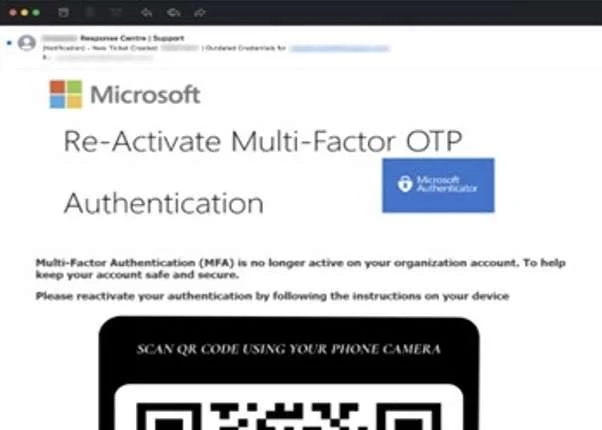
Deceptive attachments
Sometimes the phishers send scam attachments. This often happens when targeting victims whom are employeed by companies. In companies, it’s normal to send emails with attachments in different formats. Employees are familiar with opening all email attachments, without thinking about it. If the cyber-criminal sends out an email with a document called ‘final reminder’, the employee might then have a higher stress level. So, without even thinking about phishing, open it and send it to accounting. In the background of the file, there is malware which can now read everything written on the PC. The lesson here is to not open documents you are unsure of. Think about the sincerity of the email, and do not open the file without truly knowing the sender is verified.

Security alerts
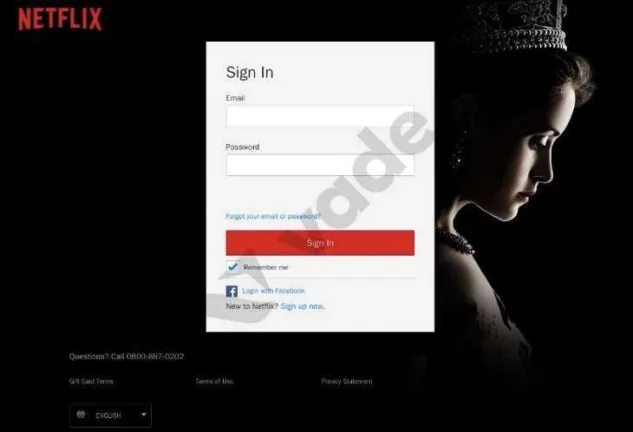
The victim receives a security alert notifying them that their password has been compromised, there is suspicious activity on an account, or they recently signed into an account from an unknown device.
For example, a user may receive an automated email impersonating Netflix—one of the most spoofed cloud brands—notifying them of unusual account activity. If victim clicks the malicious link, they’re often directed to a phishing page designed to harvest credentials that allow attackers to hack a Netflix account.
Pirated accounts from Netflix and brands like Netflix, Hulu, DirectTV, Brazzers and others commonly sell on the dark web.
Dubious links
Another method of hackers is to lead the victim to a scam website via a phishing email. The phishing email asks you to click on a link to a website which seems to be the real website of a company. Often the link pretends to be the real website, but there is a subdomain inside, which then leads you to a fake website.
For example, the email says you have to login to Google to change your password. You normally would be lead to a website like www.google.com/login , but the URL in the email could look like google.com.login.tinyurl.co. In this case you wouldn’t be leaded to google.com, you would be leaded to tinyurl.co. This even works after a ‘/’.
On these phishing websites they often want the user to type in a password, PIN or something similar. If you get an email like this, you shouldn’t use the link in the email. If you want to be sure, that no one stole your credentials, you should go to the website via typing in the URL by yourself in your browser.
Fake form fields
On those scam websites, there is another possibility to get access to your sensible data. Do you have problems with remembering long numbers? So glad that you can save your credit card information to Google, so you never have to type in the number anymore? But watch out! There is a big risk with auto fill forms Google, Safari and all the other services offers you.
The hackers can place a form on a website outside of the visible area, where you ask for the credit card information. So, the cybercriminal leads you to their fake website, and there you are asked to type in your name. Google proposes to you to use his auto fill form. What you don’t see is the credit card form, which automatically also gets filled. Don’t save your credit card details to an auto fill tool.
Language
If you are an American, you have your money in a US bank. Now you get an email, which seems to be from your bank, but is written in Spanish. Now ask yourself, why would they write you a Spanish email, even if they know you are speak English? You are right, there is a high risk. This is a scam attack and you should not react. Additionally you should be skeptic if you even get an email with important data from your bank, because normally they would send it via direct email or in your bank account inbox.
Sextortion
Sextortion scams are designed to trick victims into believing a hacker is in possession of compromising information, such as webcam video of the victim watching online pornography. These scams often target consumers of sites. The victim is instructed to pay the hacker in Bitcoin to avoid the information being leaked to the public and their acquaintances.
Corporate phishing attacks
Phishing was once considered a consumer problem when it first emerged in the mid-1990s and hackers impersonated AOL employees to exploit users of the Internet service. But as attackers grew more sophisticated, they began targeting businesses, including cloud service providers, financial institutions, and other large corporations relied upon by organizations.
By 2013, phishing became the primary vehicle for delivering ransomware, an effective threat for seizing critical data and holding organizations hostage in exchange for a fee.
Private information
Cyber-criminals try to steal your personal data. They are looking to get passwords, PIN’s and TAN’s. A bank never would ask you for such data in an email. If there is a question for this data, you can be sure you have received a phishing email. This is also a reason banks send all important things via postal … or in the inboxes of their own banking apps/internet-portales.
Grammatical and orthographic deficiency
Also, you should look out if there are misspellings or grammatical errors in sentences. Often phishing emails are originally written in another language, and then simply translated with an online translator. Because of this there are often many mistakes in phishing emails.
How to protect against phishing?
To protect against phishing, it’s best to trust in professional IT security solutions.
Implement email authentication
Email spoofing is a foundational strategy of phishing scams. Email authentication protocols exist to limit the ability for hackers to impersonate senders. Email authentication protocols, including Sender Policy Framework (SPF), Domain-Keys Identified Mail (DKIM), and Domain-based Message Reporting and Conformance (DMARC)—act as an important layer of security. Detailed recommendations for implementing SPF, DKIM, and DMARC can be found from NIST, and there are numerous resources and vendors available to assist with adopting DMARC.
Adopt an email and web browsing policy
In addition to user awareness training, an email and web browsing policy addresses the human element of your overall security posture. These policies define the safe and responsible use of email and the Internet within your organization, establishing rules and guidelines for handling sensitive information and adhering to security protocols. You can start by using a respected institution’s template and customize it to suit your organization’s unique needs. Ensure that the policy is easily accessible and incorporated into employee training.
Embrace user awareness training
Human error remains the top contributing factor to data breaches, according to Verizon’s Data Breach Investigations Report. User awareness training helps limit the potential for human error by teaching users to identify and properly handle the latest phishing threats and techniques. The best training results come from programs that provide simulation-based instruction electronically, automatically, and on-demand as users need it. Programs should also contextualize training according to the unique role of each user, considering that phishing threats can vary depending on the profession and seniority of a targeted victim. This contrasts with traditional training programs, which use generic simulation scripts, follow a pre-determined schedule, and require direct facilitation by an administrator.
At the same time, user awareness training programs should teach users to report suspicious emails. This gives admins the opportunity to investigate and remediate potential threats.
Enable Multifactor Authentication (MFA)
Multifactor Authentication (MFA) fortifies your security by requiring users to authenticate their identity through multiple means that each offer a level of security. Institutions like CISA recommend all organizations adopt MFA, especially small-to-midsized businesses. Best practice is to adopt a FIDO or PKI-based MFA, which offers phishing-resistant protection. If these options are not feasible, the next-best alternatives are app-based, SMS, or voice MFA.
Adopt and enforce strong password policies
Compromised accounts are often exploited in phishing or Business Email Compromise (BEC) attacks. Strong password policies can mitigate the risk of users creating weak passwords or reusing them across applications. To create a robust password policy, require users to set long and unique passwords, as length is more important than complexity, according to the National Institute of Standards and Technologies (NIST). Limit the number of incorrect password attempts allowed and develop and enforce a list of unacceptable passwords that includes dictionary terms, specific names, and breached credentials.
Adopt a third-party, integrated email security solution
Integrated email security solutions are highly recommended for countering modern email threats. According to the Gartner Market Guide for Email Security, businesses should supplement the native features of their email platforms with this technology, replacing traditional solutions like secure email gateways (SEGs). SEGs operate outside an organization’s internal network and rely on technologies that base detection on past attacks, rather than those that have yet to find a victim. Integrated solutions solve these deficiencies. They exist within the internal network and provide protection for external and internal attacks. Many also leverage AI-powered algorithms to detect and neutralize threats that have yet to emerge. The best solutions provide advanced capabilities for threat prevention, detection, and response.
Does your email security solution protect you from a phishing attack?
Companies getting more and more often victims of phishing email attacks. Because of the high revenue the attackers can make from companies, they try to reach out to companies with their scam. The damage, those attacks can make is immense high. Therefore, you should think about your email security.
Our security services are here to protect your company.
To secure your company the developers of Hornetsecurity invented Advanced Threat Protection. ATP can recognize harbingers of phishing mail attacks and especially can recognize targeted attacks, which are leading to only one person.
How can I prevent phishing?
Phishing isn’t malware, it is a scam tool hackers use to trick the security of the victim via personal appeal. Because of this there is no possibility to remove phishing attacks. If a hacker has your email address, he always can use it to send you phishing emails. You only can prevent to get more phishing emails.
To prevent phishing the first thing you can do is to sensitize yourself and/or your employees, to look even more precisely on emails which forces you to give out personalized data. If you did this, you and/or your employees could recognize all phishing attacks. To sensitize you can use all recognizing techniques I showed you above. To test your knowledge, google invented a quiz: https://phishingquiz.withgoogle.com/ That should minimize the danger, but anyways there remains a risk, if you don’t trust in a professional IT-Security solution.
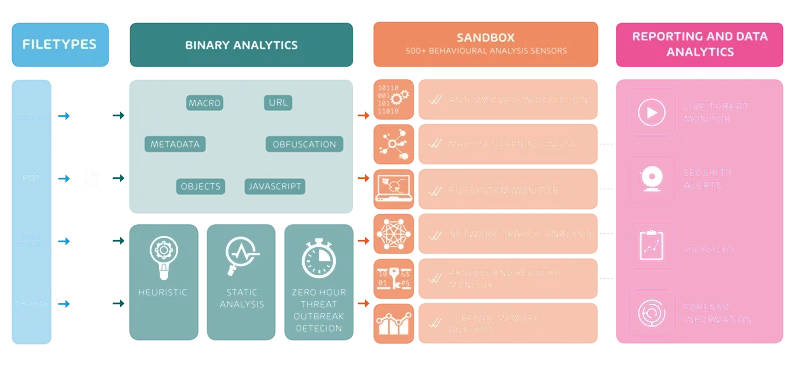
How ATP is working
Hornetsecurity ATP checks every incoming email for malicious content. To check them ATP puts all incoming files, URL and so on into a sandbox. In the sandbox ATP is running the content in virtual operating systems. Then ATP looks for effects in the systems and other anomalies. If everything is normal, then the recipient gets the email normally. When ATP detect malicious content it will block it and the recipient gets a security alert.
How to improve IT security with Security Awareness
Employees are on the first line when attackers try to exploit technical or human vulnerabilities. By training your employees companies reduce the risk of becoming a victim of cyberattacks. The Security Awareness Service from Hornetsecurity offers automated Security Awareness Training and phishing simulations.
All information summarized
The following Infopaper on phishing clearly summarizes the recommendations of the Hornetsecurity experts. Download now and get access to tips on detecting and preventing phishing attacks and recommended actions for the worst case scenario.
Learn about HORNETSECURITY’S SERVICES
Interested in Related Topics?
Did you like our contribution to phishing? Then other articles in our knowledge base might interest you as well! We help you learn more about cybersecurity related topics such as Emotet, Trojans, IT Security, Cryptolocker Ransomware, Phishing, GoBD, Cyber Kill Chain and Computer Worms.



