

Emotet
WHAT IS EMOTET? HOW CAN I PROTECT MYSELF?
WHAT IS EMOTET?
Is Emotet a Virus? No. Emotet is a type of malware that was originally designed to compromise financial data via banking trojans. Emotet first appeared as a banking Trojan in 2014. The attack aimed to intercept online access data from German and Austrian banking customers. However, Emotet can also load and execute a large number of modules with other malicious functions. Emotet strikes mainly via spam e-mail and hits private users as well as companies, hospitals, government institutions and critical infrastructure.
How does emotet work?
Typically, Emotet malware is distributed through phishing links, malicious Microsoft Office macros, and password-protected .ZIP files. Once a user downloads Emotet, the virus begins collecting credentials and data to launch subsequent attacks. This includes sending itself via spam emails to a user’s contact list or replying to existing email threats with phishing threats. The latter technique, known as thread hijacking, makes it very difficult for potential victims to differentiate between a legitimate and nefarious sender.
Methods of highly professional advanced persistent threat attacks are adapted and automated. Cyber criminals work hard to preserve their capacity to act in the infected system for as long as possible. It is therefore not easy to remove Emotet.
One aspect makes Emotet particularly dangerous: Since the end of 2018, the malware has been able to use so-called Outlook harvesting to read the contact relationships and e-mail content from the mailboxes of infected systems in order to initiate further attacks. This means it is spread particularly quickly. New recipients then receive equally authentic-looking e-mails from people with whom they have recently been in contact. Damaged file attachments or URLs contained in the message are opened carelessly. Emotet continues to pose a threat to organizations and users today, though the threat was most prominent in 2019.
In addition to this spam module, Emotet can also load a worm module through which it spreads in the company network. In this way, it can settle on other computers without users having to click and activate an attachment. In this context, Emotet also undertakes brute force attacks with the aim of cracking passwords. This can have serious consequences. Once the computer is infected, Emotet downloads further malware via the C&C server, depending on the target. There is a risk of data theft, loss of control over systems, the failure of the entire IT infrastructure and restrictions in critical business processes. In extreme cases, entire company networks have to be rebuilt after an infection. The damage often runs into the millions.
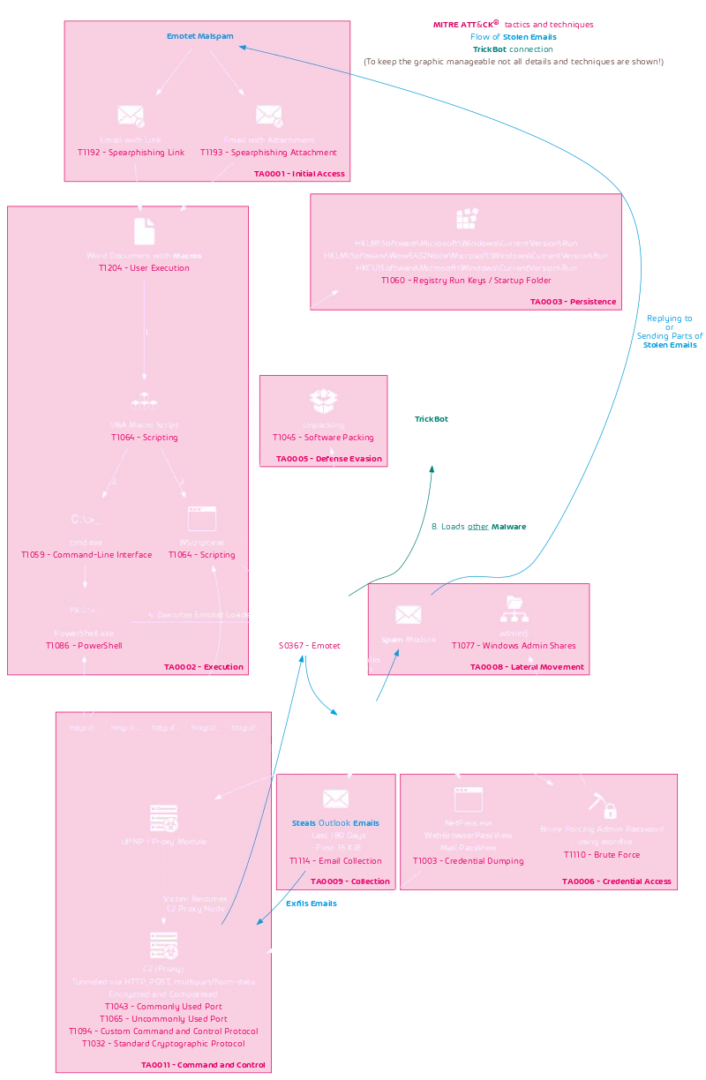
EMOTET CHAIN OF INFECTION
At least the initial part of the Emotet infection chain and the tactics and techniques used, as defined in the MITER ATT & CK Framework, are shown in the following flow chart:
It should be emphasized that Emotet steals emails from victims and uses them as templates for new malspam. It uses so-called email thread hijacking, in which it replies to old email conversations with a malicious email. There is a high probability that e-mails from known people will be opened in existing conversations. As a result, Emotet’s distribution campaigns are very successful. This type of attack is one of the main reasons why IT security managers need to invest in security awareness training in order to create awareness of this threat.
Emotet is also so dangerous because, in addition to its own modules to steal emails, misuse computers and act as a C2 and spam server, it also delivers other malware such as TrickBot, which can ultimately lead to infection with Ryuk ransomware. Even if you try to clean up the Emotet infection, additional malware may already be running on the system.
When a system becomes infected with Emotet, it becomes part of the Emotet botnet.
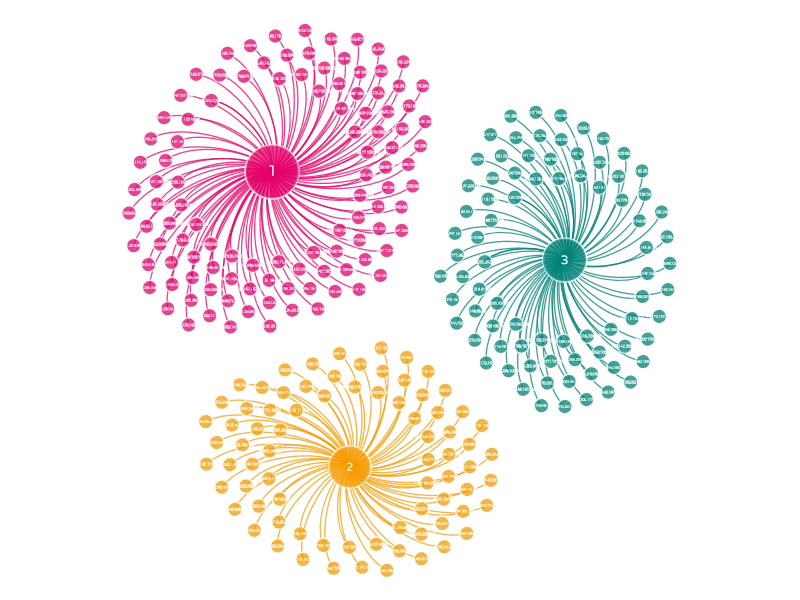
EMOTET BOTNET
The Emotet botnet is divided into several botnets. Researchers named them Epoch 1 and 2 because they received payload updates at different times. Each Epoch has its own unique RSA key that is used for C2 communication. On September 17, 2019, part of the Epoch 1 botnet was split off into the Epoch 3 botnet.
Each botnet connects to the C2 servers of its Epoch. When a recipient is infected by an Emotet document belonging to Epoch 1, the document downloads the Emotet loader from the Epoch 1 infrastructure and then becomes part of Epoch 1.
The current structure of the Emotet botnet’s Tier 1 C2 server is as follows:
Changes are first implemented in the E2 botnet. It is possible this was done as a test to ensure that in the event of changes introduced that do not work, only a portion of the entire botnet is lost.
MASTER OF DISGUISE: WHY EMOTET IS SO DIFFICULT TO FIGHT
Emotet is not easy to identify and intercept because it deceives conventional antivirus products: As a polymorphic virus, the code changes slightly each time it is called up in order to avoid detection by signature-based virus scanners. The virus also detects when it is running in a virtual machine. As soon as a sandbox environment is registered, the program falls into a kind of stand-by mode and does not take any harmful actions at that moment.
Emotet, TrickBot and the Ransomware Ryuk
As already mentioned, Emotet loads further malicious programs after a successful infection. A particularly dangerous alliance arises in the interaction with TrickBot and Ryuk. Disguised in a Word document, Emotet penetrates a company network while executing the file and scouts it. As a “door opener,” it reloads the TrickBot banking Trojan, which copies account access data among other things. It forwards this information to the Ryuk ransomware, which is the last to be downloaded. Ryuk now encrypts all files in the system that TrickBot and Emotet previously classified as sensitive or important.
HOW CAN YOU PROTECT YOURSELF FROM EMOTET?
Protecting yourself against Emotet requires a multi-layered approach. Consider adopting integrated email security that can protect against polymorphic and environmentally aware malware, which can change depending on its environment. Regularly update your operating system and applications to patch any vulnerabilities that Emotet could exploit. Additionally, educate your teams and clients about email security best practices, such as avoiding clicking suspicious links or downloading attachments from unknown sources.
In order to protect yourself effectively against Emotet, you have to concentrate primarily on the main gateway of the malicious program: e-mail communication. Hornetsecurity Advanced Threat Protection easily detects Emotet and Ryuk in e-mails and quarantines both malware programs. The Emotet Trojan is identified in the first analysis instance. The downstream Trojans Ryuk and TrickBot can be unmasked using the dynamic behavior analysis in the ATP sandbox. E-mails containing the perfidious malware are not delivered to the recipients.
Furthermore, basic, safety-conscious behavior must be observed:
- Since Emotet often hides in Microsoft Office files and needs macros in order to be able to install malicious programs, it makes sense not to allow them. In private as well as in most business areas, they are not required. If you still cannot do without macros, it is possible to only allow those that are signed.
- Any security updates that are deployed must be installed immediately for operating systems, anti-virus programs, web browsers, e-mail clients and Office programs.
- Regular data backups are recommended.
- Vigilance is the top priority: Even with supposedly known senders, you should be careful with file attachments to emails, especially Office documents and the links they contain. When in doubt, it is advisable to seek direct contact with the sender of a suspicious e-mail and check the credibility of the content.
- Access to the company’s own network should be continuously monitored, because this way it can be determined in good time whether an Emotet infection has occurred.

Increasing Threat From Ransomware
Ransomware is one of the most popular cybercriminal methods to make big profits and cause immense (financial) damage to the victims. If the ransomware gets into a company’s system, all sensitive and company-confidential files are encrypted and only released again if a ransom is paid in the form of bitcoins. Even worse, it is not always clear whether the files will actually be released after payment.
Most popular targets for hackers are large companies and government institutions as well as critical infrastructure. In the worst case scenario, an attack threatens bankruptcy. However, significant losses in sales are also possible effects.
LEARN MORE ABOUT EMOTET
The info paper clearly summarizes the recommendations of the Hornetsecurity experts on the subject of Emotet. Download now and find out what it is, what exactly makes the malware so dangerous and how users can protect themselves from Emotet.
Learn about HORNETSECURITY’S SERVICES
Interested in Related Topics?
Did you like our contribution to Emotet? Then other articles in our knowledge base might interest you as well! We help you learn more about cybersecurity related topics such as Emotet, Trojans, IT Security, Cryptolocker Ransomware, Phishing, GoBD, Cyber Kill Chain and Computer Worms.


