

10 Most Common Types of Cyber Attacks You Should Know About
The best way to protect your digital life is to assume it’s going to be hacked. In practical terms, it is essential to implement various cybersecurity measures before your data is compromised. Once your data is compromised, it may be too late to fully mitigate the damage. However, taking necessary actions even after a data breach is crucial.
Since the start of the COVID-19 pandemic, the number of cybersecurity attacks has significantly increased due to the widespread adoption of remote work. It is crucial to be aware of the most common types of cyber attacks and gain valuable insights into the topic. Here, we will list 10 of the most common cyber attacks that you should know about.
Let’s first start by clarifying some basics about cybersecurity.
What Is a Cyber Attack?
By definition, ‘cyber’ refers to anything related to computers, information technology, and the Internet. It is also associated with protecting computer networks and hardware from attacks.
These attacks aim to compromise data, destroy or steal it, and disrupt business services. The disruption of business services often leads to financial losses and decreased customer satisfaction.
Cybersecurity attacks are carried out by individuals or groups known as hackers, attackers, or hacker groups. Each of these entities has different target groups. Some may focus on attacking corporate businesses, while others may target governments.
Why do they do it? For fun, financial gain, and their own or someone else’s goals (espionage, revenge, challenge, and others).

In many cases, hacking attacks are made possible due to human errors or vulnerabilities in software systems. An example of such an error is the recent discovery by security company Vectra about Microsoft Teams. According to Vectra, Microsoft Teams stored authentication tokens in unencrypted plaintext mode. This flaw could potentially allow attackers to gain control over communications within an organization.
IT security is a crucial factor to protect your infrastructure from cyber attacks.
What Is a Cyber Attack?
Cybersecurity attacks happen while I was writing this article and while you are reading it. There is no exact number we can provide for the frequency of cyber attacks due to the fact that they occur 24/7, and the numbers can vary due to the constantly evolving nature of cyber threats. It’s a non-stop activity initiated by malicious individuals or groups.
What Happens During a Cyber Attack
What happens during cyber attacks solely depends on the type of attack. In general, malicious individuals or groups aim to gain unauthorized access to your systems, applications, networks, or hardware and steal or destroy confidential information.
For instance, if the attackers aim to destroy your data, they may employ ransomware to encrypt it, making it inaccessible. If you want to access it, you have to pay for it. If not, data are not usable at all.
On the other hand, if their intention is to steal your data, they will transfer it to their own servers or systems and expose it publicly. In either scenario, the consequences can be disastrous for the affected parties.
To protect your system against such scenarios, it is crucial to implement cybersecurity measures and maintain regular backups of your data.
What Happens During a Cyber Attack
There are numerous types of cybersecurity attacks, even exceeding 100. However, many of them are variations or derivations of the most common attacks. In this section, we will address the 10 most common cybersecurity attacks, provide you with some statistics, and offer tips on how to protect your infrastructure and maintain peace of mind.
Let’s unpack the 10 most common cybersecurity attacks we can see today.
Malware attacks
Back in the days when we used to discuss cybersecurity attacks, we would often mention viruses, spyware, trojans, backdoors, and so on. These are all distinct types of malware that aim to gain unauthorized access to systems, hardware, and data to infect them.
In the year 2000, the ILOVEYOU worm, rapidly infects millions of Windows machines shortly after its release, spreading quickly like wildfire. The ILOVEYOU worm was not the first-ever malware attack developed, but it is one that remains memorable to many.
Did it start with ILOVEYOU worm? It didn’t. Malicious people began creating scripts that could alter program behavior long before the advent of the ILOVEYOU worm, with the first program.
There are different types of malware attacks, including viruses, worms, Trojans, ransomware, spyware, adware, botnets, keyloggers, rootkits, and backdoors. Ransomware is one of the most popular and destructive malware. You can read more details here What is ransomware? How can you protect against Ransomware?
According to our research, 20% of all reported Ransomware Attacks occurred in the last year, the survey finds. Find our takeaways in our article Ransomware Attacks Survey 2022.
There are different ways to protect your machines, including running antivirus software with real-time protection, host-based firewalls, a fully patched operating system, and secure hardware and applications.
One of the most important aspects in addition to these measures is security awareness training for employees or end users. Read more here Forgetting Curve according to Dr Ebbinghaus: Why cyber awareness training is an ongoing process.
We cover you with 7 reasons why security awareness is critical for employees. You can read more here 7 Reasons Why Security Awareness Is Critical for Employees.
Phishing Attacks
Phishing attacks are one of the most common types of attacks that we receive on a daily basis via email. These are the emails that ask you to verify your Facebook or LinkedIn account, change your banking credentials, and others.
One of the common ways to deliver a phishing attack is via email. However, they can also be delivered via SMS, voice, website, spear, and other methods.
According to our Cyber Security Report 2023, phishing ranked the number one email attack technique, at 39.6% of detected attacks.
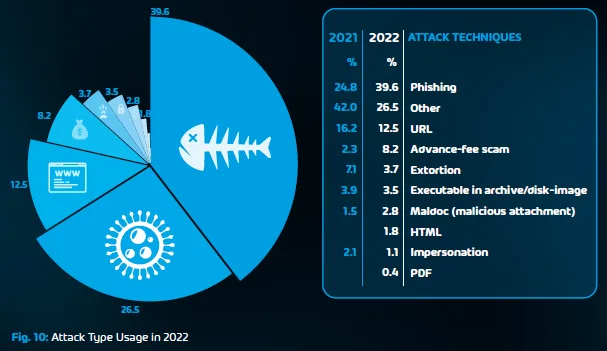
You can prevent this kind of attack by educating your employees about what to open and what not to open. Additionally, having phishing detection tools is a must-have.
Did you hear about QR code phishing? We did write and article and produced video to give you insight what QS scam is and how to stay protected. You can read it here All You Need to Know About QR Code Scams.
If you would like to explore more about phishing, read it here Phishing – The danger of malicious phishing mails.
Distributed Denial of Service (DDoS)
You have probably heard of or experienced situations where a certain website was not available because it was overloaded with too many requests. In normal, let’s call it legal circumstances, this happens because IT did not predict the bandwidth and number of requests. This can be fixed by assigning more resources to the server hosting your web application.
From a legal perspective, a website or service becomes inaccessible when it is overwhelmed with a flood of unsolicited traffic. However, this traffic is not generated by legitimate users but by attackers. Since the website or service cannot respond to all requests, it becomes unavailable. This is known as a Distributed Denial of Service (DDoS) attack.
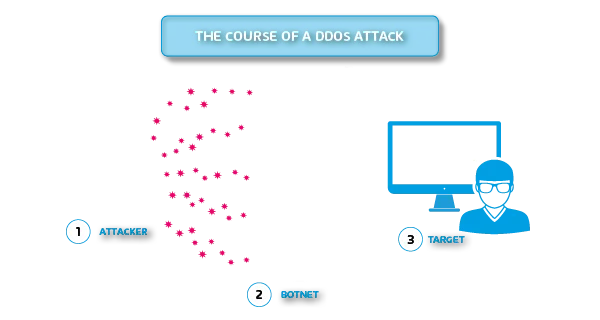
There are different ways to protect against DDoS attacks. The first one is to allocate enough resources to the server hosting your web application. Then, implement DDoS mitigation services and enhance network and infrastructure security.
Man-in-the-Middle (MitM)
If you can use secure protocols, do so. By using secure protocols in client-server communication, the exchanged traffic is encrypted, preventing malicious individuals from reading it in plain text.
This is why every vendor recommends using HTTPS instead of HTTP. In practical terms, if you were to log in to an HTTP site, a hacker would be able to see your credentials in plain text. That is something we want to avoid, right?
When hackers come between the client and server and intercept the traffic, that type of attack is called a Man-in-the-Middle (MitM) attack.
There are different ways to prevent MitM attacks, including using secured protocols (e.g., HTTPS and FTPS instead of HTTP and FTP), employing PKI (Public Key Infrastructure) and certificates, monitoring traffic, and others.
Even if you use secure protocols, you should ensure that MitM attacks cannot occur. For example, avoid connecting to open WiFi networks, or if you are an IT admin, disable open WiFi networks.
Password attacks
We wouldn’t be happy if someone had a key to our house or office, allowing them to unlock the door, enter, and compromise our personal belongings. The same principle applies to our digital infrastructure. An easily guessable or simple password serves as a key for hackers to gain access to our corporate systems.
If you are an IT admin, it is important to enforce various password policies to ensure stronger security. For example, requiring a minimum password length of 10 characters, prohibiting the use of default or old passwords, implementing password expiration and minimum age requirements, and promoting the use of multi-factor authentication.
By implementing these measures, you can significantly enhance the security of your systems and reduce the risk of unauthorized access or data breaches.
According to The Weak Password Report 2022 and 2000 surveyed professionals:
- 93% of the passwords used in brute force attacks include 8 or more characters.
- 54% of organizations do not have a tool to manage work passwords.
- 68% of passwords used in real attacks include at least two-character types.
- 48% of organizations do not have user verification in place for calls to the IT service desk.
- 42% of seasonal passwords contained the word “summer”.

The enforcement of password rules is the responsibility of the IT teams. However, end users should be trained on how to create passwords properly.
SQL Injection
Many applications and websites store data in databases. SQL (Structured Query Language) is a common language used to interact with databases. SQL injection is a type of attack where a malicious person compromises the data within the database. The attacker injects malicious SQL code into user inputs, which is then executed by the application’s database. Through this attack, the attacker gains unauthorized access to the SQL database.
There are different ways to protect your SQL database from this type of attack, including using a Web Application Firewall (WAF), implementing secure development practices, conducting security testing and auditing, implementing monitoring and logging, and utilizing other measures.
DNS Spoofing
DNS (Domain Name System) is a protocol used in computer networks to translate human-readable website names into IP addresses and vice versa. For example, instead of entering 172.217.20.14 into your preferred web browser to access Google, you enter google.com.
DNS spoofing refers to altering the DNS server and redirecting users to malicious targets. Practically speaking, when a user tries to reach a certain website or target, the attacker would redirect them not to Google.com, but to a malicious endpoint (Gooogle.com). Do you see a difference!?
There are different ways of protecting infrastructure from this type of cyber attack including DNSSEC (Domain Name System Security Extensions), using secure DNS resolvers, regular DNS cache flushing, firewall and Intrusion Detection Systems (IDS), and others.
Cross-Site Scripting (XSS)
This type of attack is commonly found on websites and web applications. Attackers inject malicious code into websites that are accessed by users. By doing so, attackers can steal users’ information, perform actions on behalf of the user, and disrupt website applications.
There are different types of XSS attacks, including stored XSS, reflected XSS, DOM-based XSS, and other variations. To protect a website from cross-site scripting (XSS) attacks, developers or vendors should implement proper input validation and output encoding techniques.
Regular security testing and vulnerability assessments can also help identify and mitigate XSS vulnerabilities in web applications.
Zero-Day Exploits
If you read or hear about a zero-day exploit, it means that the vendor or developer is not aware of it. It remains unknown to them until communicated by an attacker or until the network is compromised. The term “zero-day” signifies that vendors have zero days to patch or fix the vulnerability discovered by the attacker.
That is a scary event for any vendor.
In a legal scenario, ethical hackers would inform the vendor about the issue, allowing the vendor to release a patch. However, in the illegal world where attackers are involved, the vendor is unaware of the exploit, providing attackers with time to compromise the network.
Currently, zero-day exploits are sold on the dark web to attackers.
There are several ways to protect your infrastructure from zero-day exploits, including patching all the systems whenever a new update is available, implementing endpoint protection and intrusion detection systems, engaging in responsible vulnerability disclosure, and others.
Social Engineering
In the past, a famous hacker named Kevin Mitnick was able to access sensitive financial information in a US bank without using any fancy technology. Instead of hacking into systems or devices, Kevin used a technique called social engineering.
He pretended to be someone else, like a customer or an IT support person, and tricked people into giving him information. Social engineering is all about fooling and manipulating people into not being careful, sharing private information, or doing things that put their security and data at risk.
This kind of trickery is known as human error and is a major threat in the digital world.
According to World Economic Forum – The Global Risks Report 2022, 95% of all cyber security breaches are caused by human error. Malicious people try to exploit human psychology in more ways than social engineering.
Other Types of Cyber Attacks
We listed 10 common types of cyber attacks, but there are many more. Some are variations of existing cyber attacks, while others are distinct. For example, ransomware and botnets are different variations of malware. Phishing has different variations including spear phishing, whaling, smishing, vishing, pharming, clone phishing, link manipulation, content injection, malware-based phishing, and others.
On another hand, there are some other attacks including Advanced Persistent Threats (APT), insider threats, cryptojacking, supply chain attacks, eavesdropping, pharming, brute force attack, cross-site request forgery (CSRF), clickjacking, watering hole attacks, malvertising, identity theft, data breach, drive-by download, malicious email attachments, business email compromise (BEC), IoT attacks, ransomware-as-a-service (RaaS), SIM card swap fraud, QR Scams, and others.
The list is extensive.
It’s important to note that cyber-attacks are continually evolving, and new attack vectors may emerge.
Before we call it a day
To properly protect your cyber environment, use Hornetsecurity Security Awareness Service and Advanced Threat Protection to secure your critical data.
We work hard perpetually to give our customers confidence in their Spam & Malware Protection, Email Encryption, and Email Archiving strategies.
To keep up to date with the latest articles and practices, pay a visit to our Hornetsecurity blog now.
Conclusion
Cybersecurity is a 24/7 game. Attackers continuously search for exploits to compromise infrastructure, while ethical cybersecurity professionals strive to protect it. Numerous cyberattacks can occur, and addressing them all would require an extensive ebook. In this article, we focused on the 10 most common protocols and briefly discussed some of their variations.
We provided insights into cybersecurity attacks, their consequences, and frequency. We listed the 10 most common attacks: malware, phishing, social engineering, password attacks, XSS attacks, DDoS attacks, DNS spoofing, zero-day exploits, Man-in-the-Middle (MitM) attacks, and SQL injections.
Additionally, we discussed measures to help you stay protected.
One important thing to remember is that while IT enforces security policies, internal security awareness training is also crucial. Security is a shared responsibility, and everyone in an organization should be aware of and actively contribute to maintaining a secure environment.

