

1 in 4 companies reported IT security incidents in the last year, survey finds
27.6% of organizations were the target of known IT incidents in the last 12 months.

A global survey of IT professionals and leaders of over 800 organizations reveals that more then a quarter of organizations surveyed has reported being the target of a security-related incident in the last 12 months. Of these organizations that have been targeted, 71.3% are subject to security compliance requirements such as HIPAA, PCI, SOX, GDPR, and ITAR/CMMC. The survey focuses on IT security measures within organizations, along with how these measures relate to the compliance requirements created by governing bodies.
While no strict causality exists between the rate of incidents and the presence of compliance requirements, one can conclude that organizations that operate in industries or territories with a higher incidence of cyber-attacks are more likely to be regulated by compliance requirements.
In fact, the survey found that 3 in 10 organizations (30.4%) that are required to conform to compliance requirements have reported being the target of an IT security-related incident in the last year, in comparison to 22.8% of those not required to follow compliance regulations.
The high incidence of IT security-related incidents among organizations that are subject to regulatory requirements may also explain why 70.5% of organizations find it necessary to invest in IT security beyond what is mandated by compliance standards.
Attacks via email account for 71% of all reported incidents
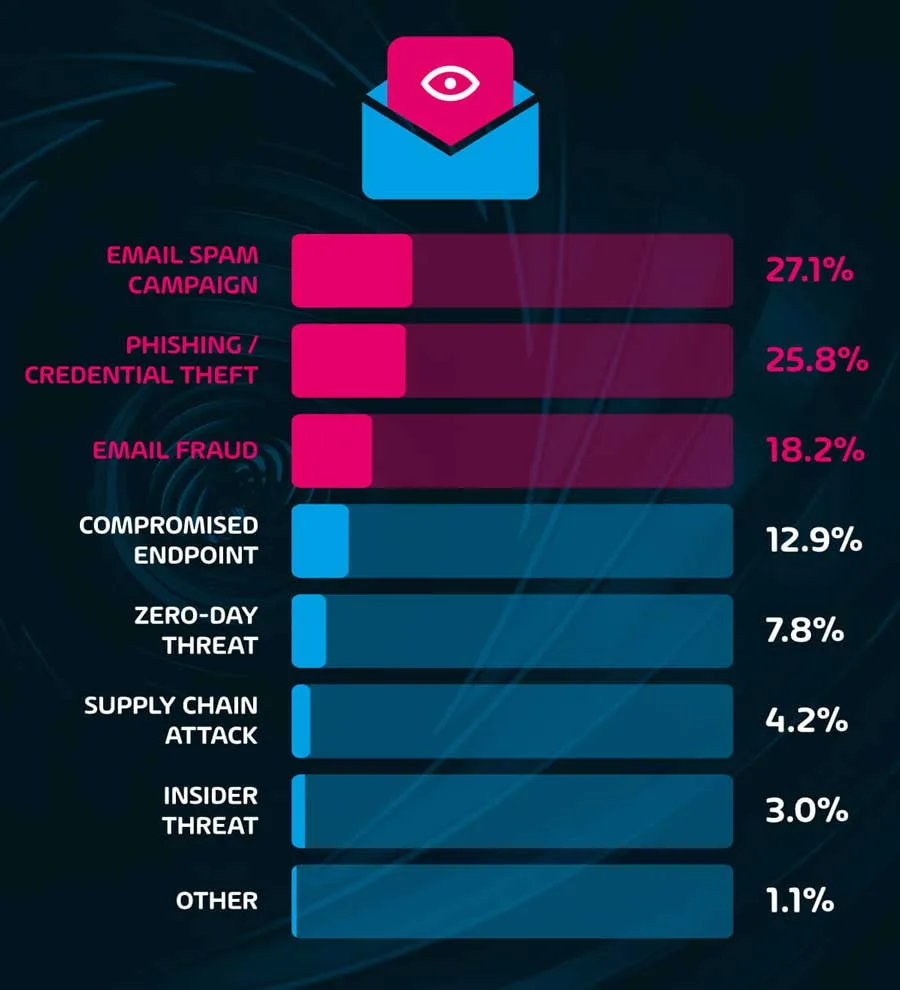
As shown in the chart above, email spam campaigns, phishing/credential theft, and email fraud are the most commonly reported known vectors of attack. This set of data reinforces our knowledge of the fact that the most common weakness among organizations is where it is easiest to communicate with end-users – email.
While compromised endpoints, zero-day threats, supply chain attacks, and insider threats were also mentioned as vectors of attack during these incidents, email remains the most attractive prospect for would-be cybercriminals.
While stock email filtering and security features offered by cloud workspace providers such as Microsoft 365 can help combat these threats, more advanced email security features offered by third party security providers can relieve pressure from internal IT departments, allowing them to focus on other business priorities.
85.6% of organizations report Ransomware as a significant security concern for the next 12 months
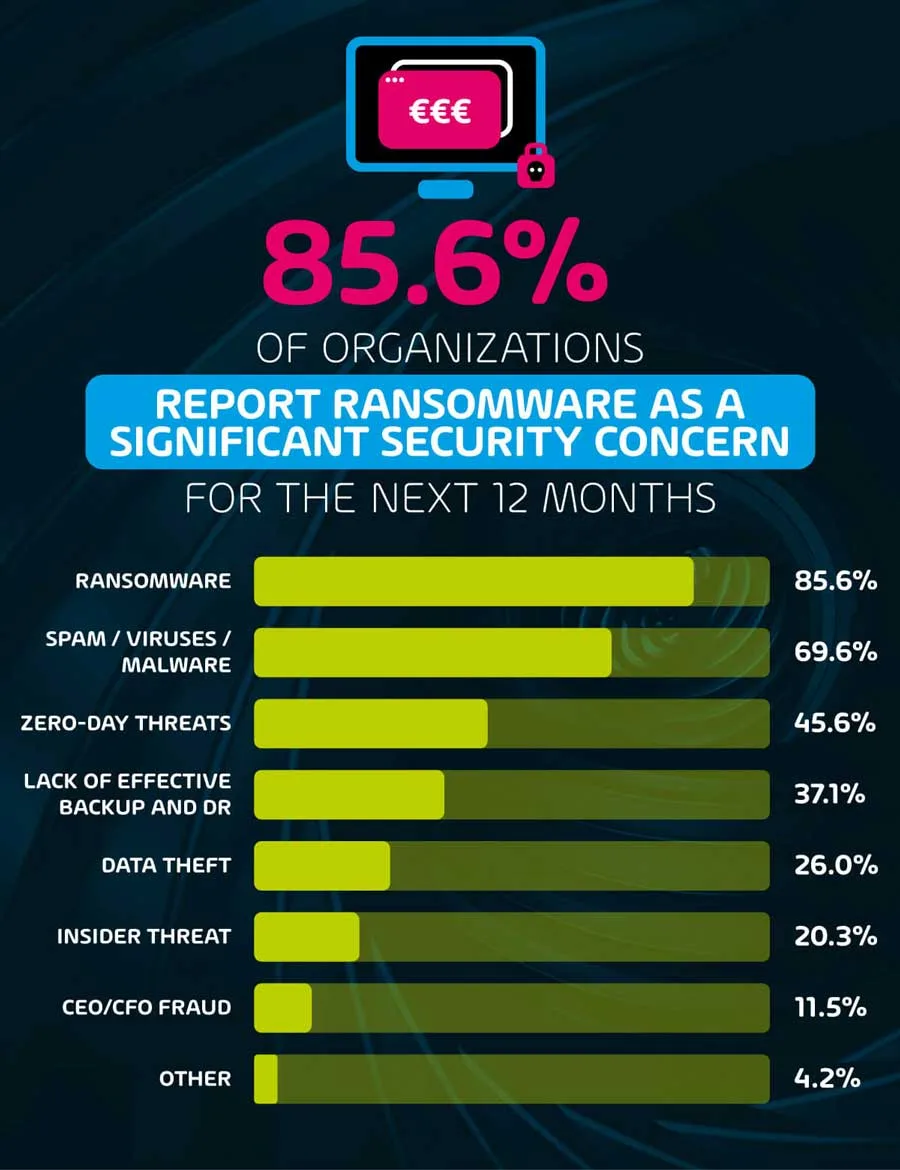
When asked about their biggest security concerns of the coming 12 months, 85.6% of all respondents listed R . Considering the previous data point highlighting email as the most common vector attack, concerns around ransomware are unsurprising. As we discussed in a ransomware survey conducted recently, 1 in 5 organizations falls victim to ransomware attacks, and the effect can be disastrous. The same survey identified email filtration and threat analysis as one of the foremost tools used by organizations to combat the risk posed by ransomware attacks.
The average downtime a company experiences after a ransomware attack is 21 days, and while the cost of that downtime alone can be fatal for many companies, that is without taking into consideration the cost of data recovery, the payment of the ransom, and long-term brand damage.
Rate of IT security incidents grows with company size
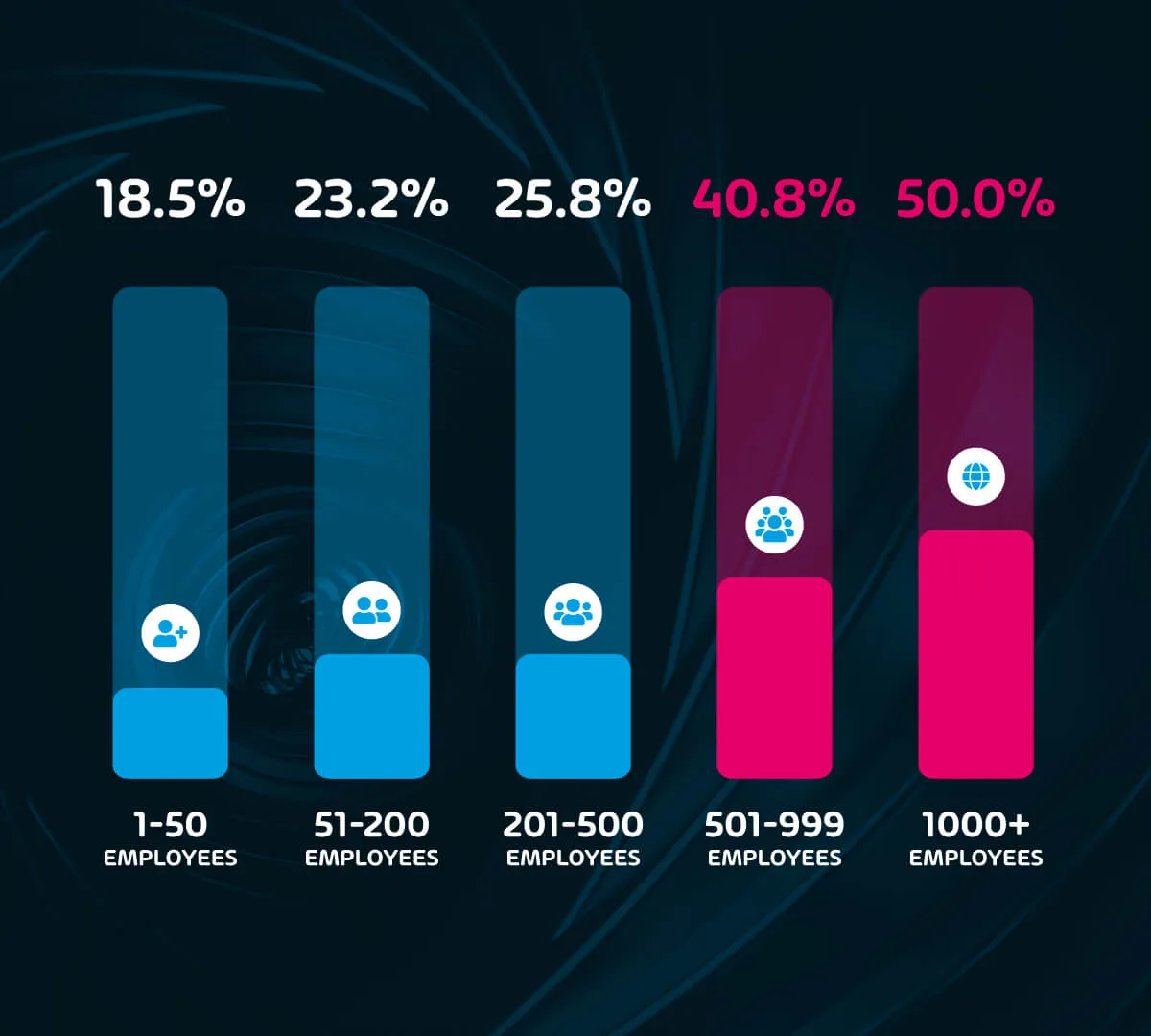
Nearly 1 in 5 (18.5%) companies with 1 to 50 employees have been the target of an IT security-related incident in the last year. While that is a worryingly high incidence rate, it is by far the lowest among all size categories documented in this survey.
23.2% of organizations with 51 to 200 employees were targeted, as were 25.8% of those with 201 to 500 employees. Organizations with 500 to 999 employees were targeted 40.8% of the time, while half of surveyed organizations with over 1,000 employees reported an attack.
This trend clearly shows that cyberattacks are common across all organizations, but it seems clear that as an organization grows, the rate at which it is targeted increases dramatically. Security efforts made while a company has less than 500 employees are evidently not enough to protect organizations as they grow beyond that number.
Use of more Microsoft 365 security features correlates with a higher rate of security incidents
4 in 5 (80.2%) of all survey respondents reported that they use Microsoft 365 in their organization. We asked these individuals which security features provided within the Microsoft 365 stack are used within their company. Unsurprisingly, Multi-Factor Authentication is the most widely used feature, with 3 in 4 respondents (73.3%) making use of it. Defender for Microsoft 365 and Conditional Access followed in popularity with 41.2% and 38.2% of respondents selecting them respectively.
The more surprising data point gathered in this regard was that the higher the number of Microsoft 365 security features that a company reported using, the higher the likelihood of said company having been the target of a security incident in the last 12 months. As displayed by the below graphic:
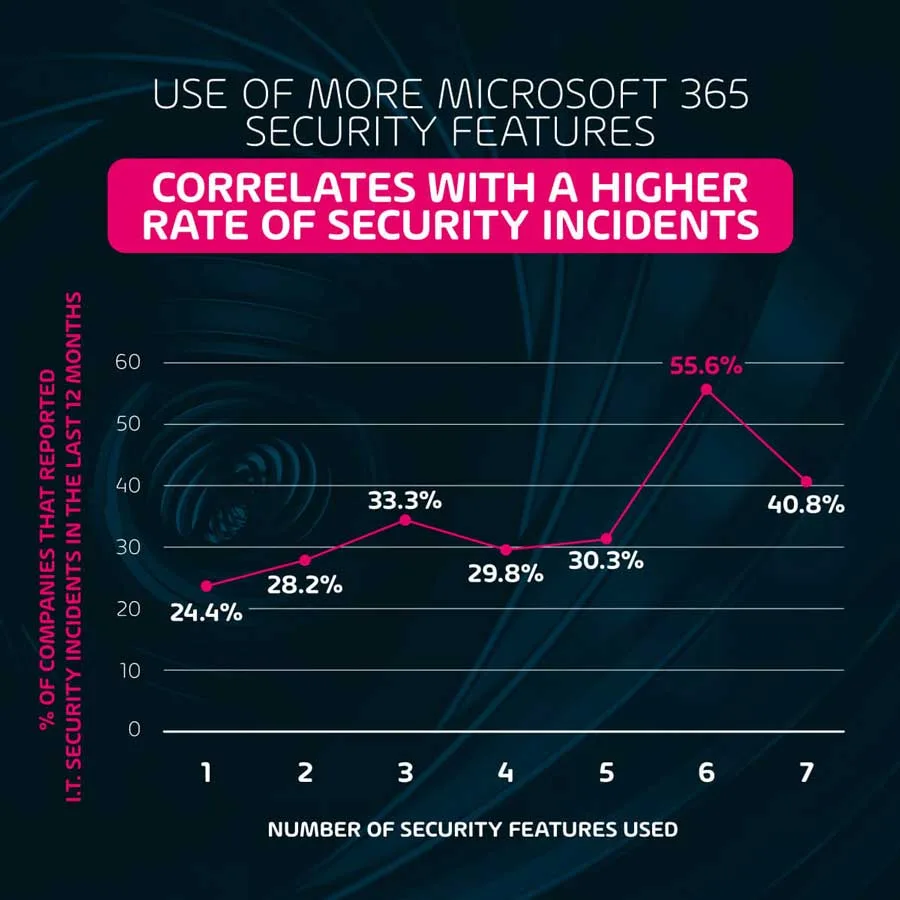
While this does not mean that Microsoft 365 security features are at fault for the higher incidence, it may indicate that using a higher number of stock security features may lull IT departments into a false sense of security, which then leads to more incidents. It may also indicate that some of the more complex Microsoft 365 security features may be currently being applied incorrectly, thus leaving holes in the defense and not providing the protection required.
The majority of organizations (69.3%) use 4 to 8 IT security measures
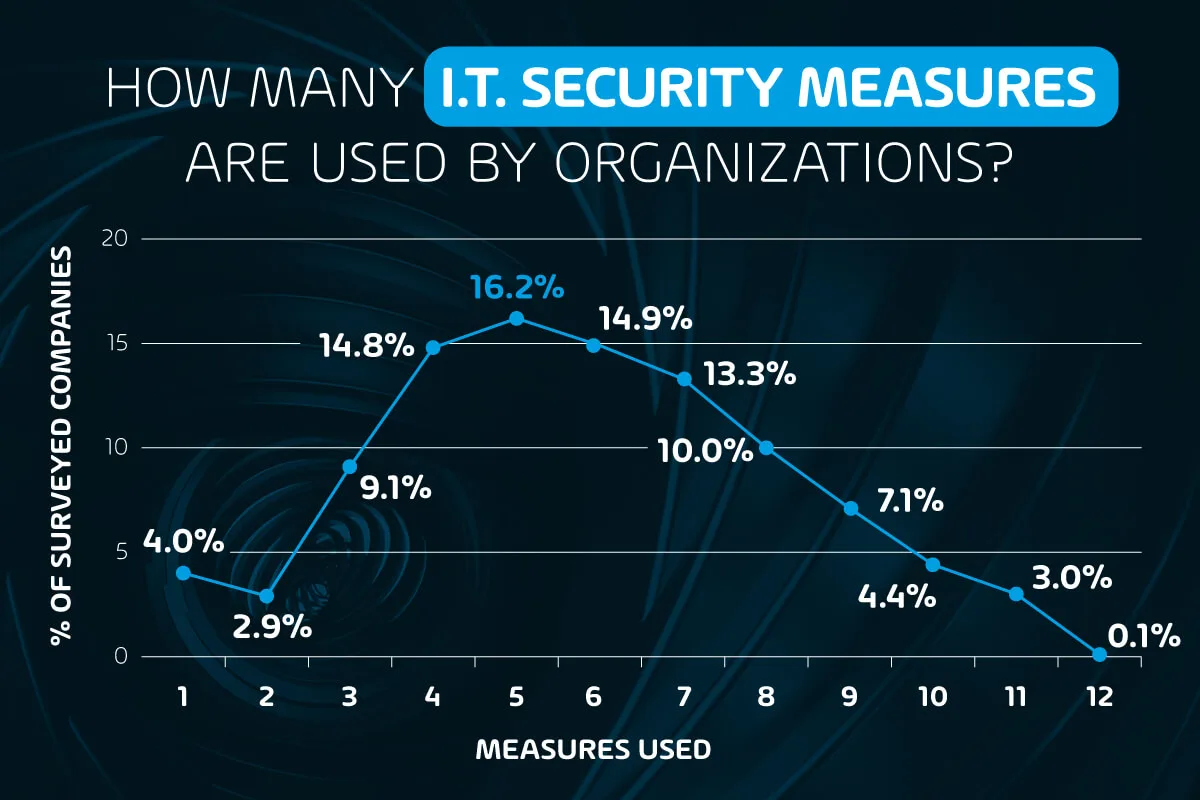
If you’re wondering just how many security measures are used in most organizations, here’s your answer. The majority of IT departments typically employ between 4 to 8 security measures, with the most common being 5, and the average being 5.8.
We also wanted to understand what kind of relationship, if any, exists between the number of security measures employed by organizations and the rate at which they encounter IT-related security risks. The following data shows the rate at which incidents occurred within organizations, based on how many security measures were being taken.
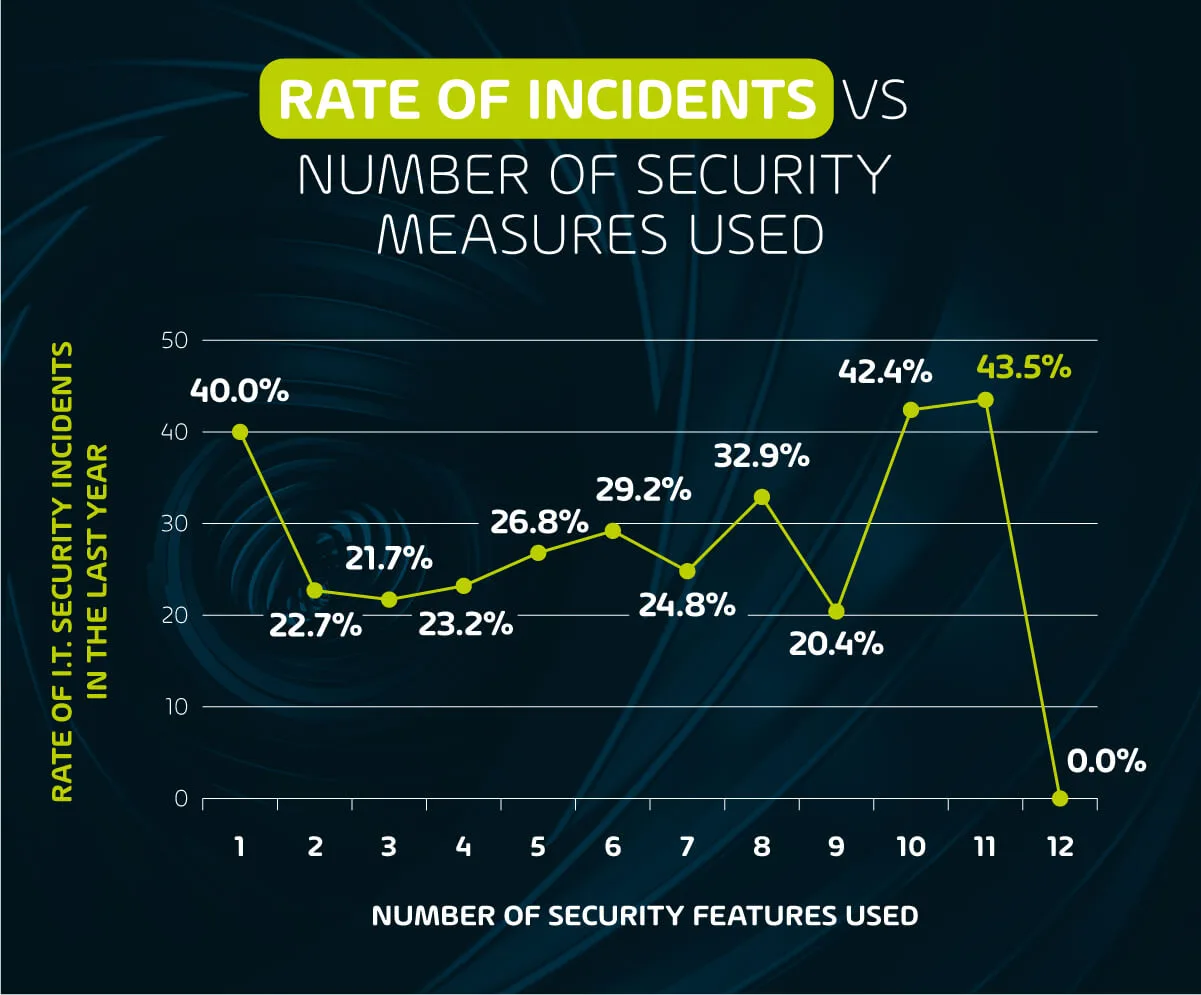
Based on the above data, we can see that the rate of incidence is highest at both extremes of the data set. Those organizations that use only 1 security measure suffer an incidence rate of 40%, which is only slightly lower than those that use 10 or 11 security measures. This indicates that the more security measures being used, the more of a target the organization is, and the more vigilant said companies must be to ward off threats.
Spam filtration is the most commonly used security (84.4%)
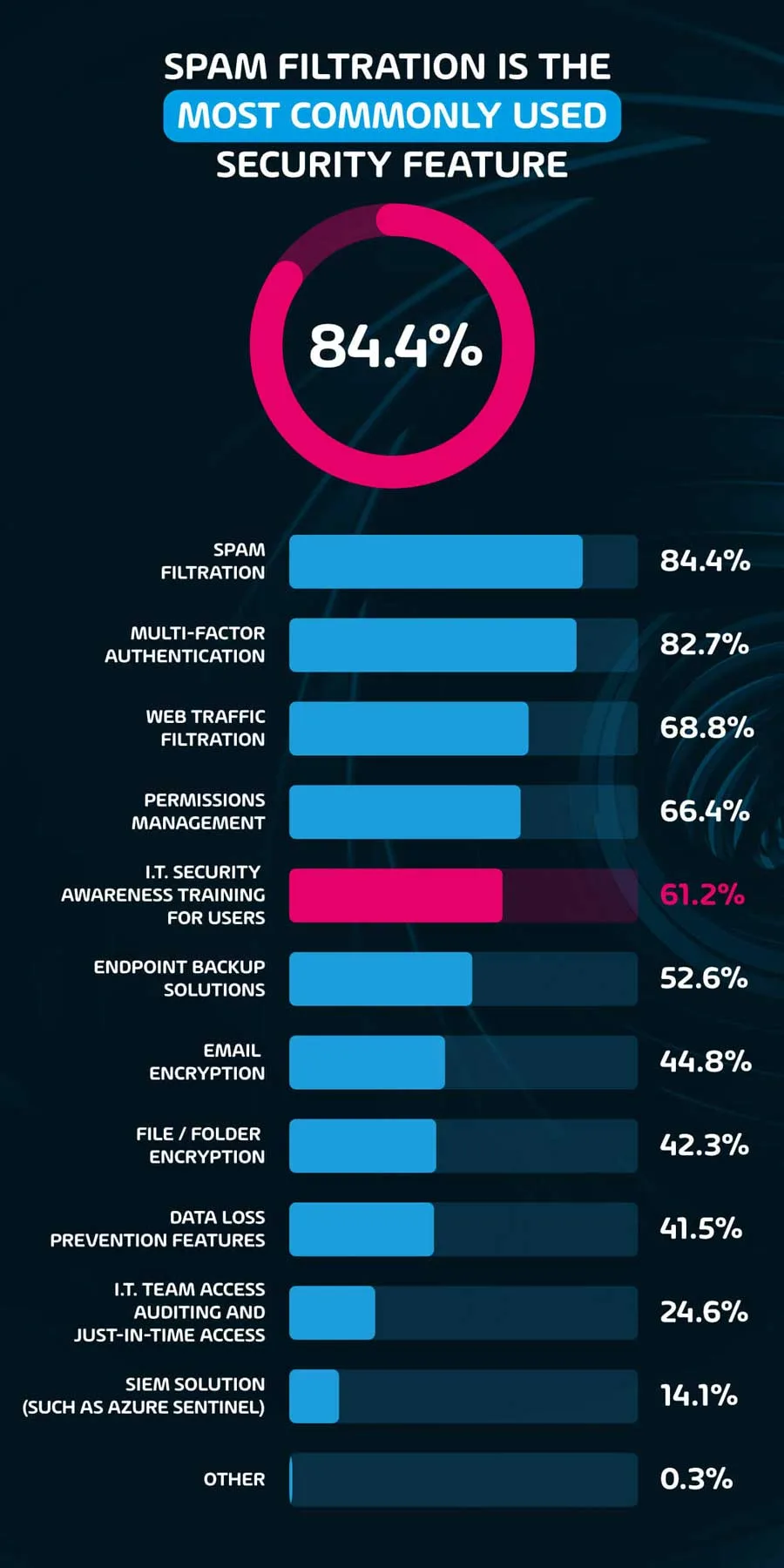
Considering that the foremost vector of attack of the known IT security incidents reported in this survey were Email Spam campaigns, this data point is unsurprising. Other highly used security methods include Multi-Factor Authentication (82.7%) and Web traffic filtration (68.8%). These methods focus chiefly on preventing security risks from reaching end-users altogether, however, what happens when these somehow fail?
Only 6 in 10 (61.2%) of organizations ensure that IT security awareness training is given to end-users to help them identify threats that have slipped through the filtering systems in place. This is a significant misstep for those organizations that do not provide such training, considering that Phishing & Credential Theft is the second most common vector of attack by cybercriminals reported in this survey, at 58.4%. Training would assist end-users in identifying and flagging potential threats and can even provide further data for the IT teams to improve security measures.
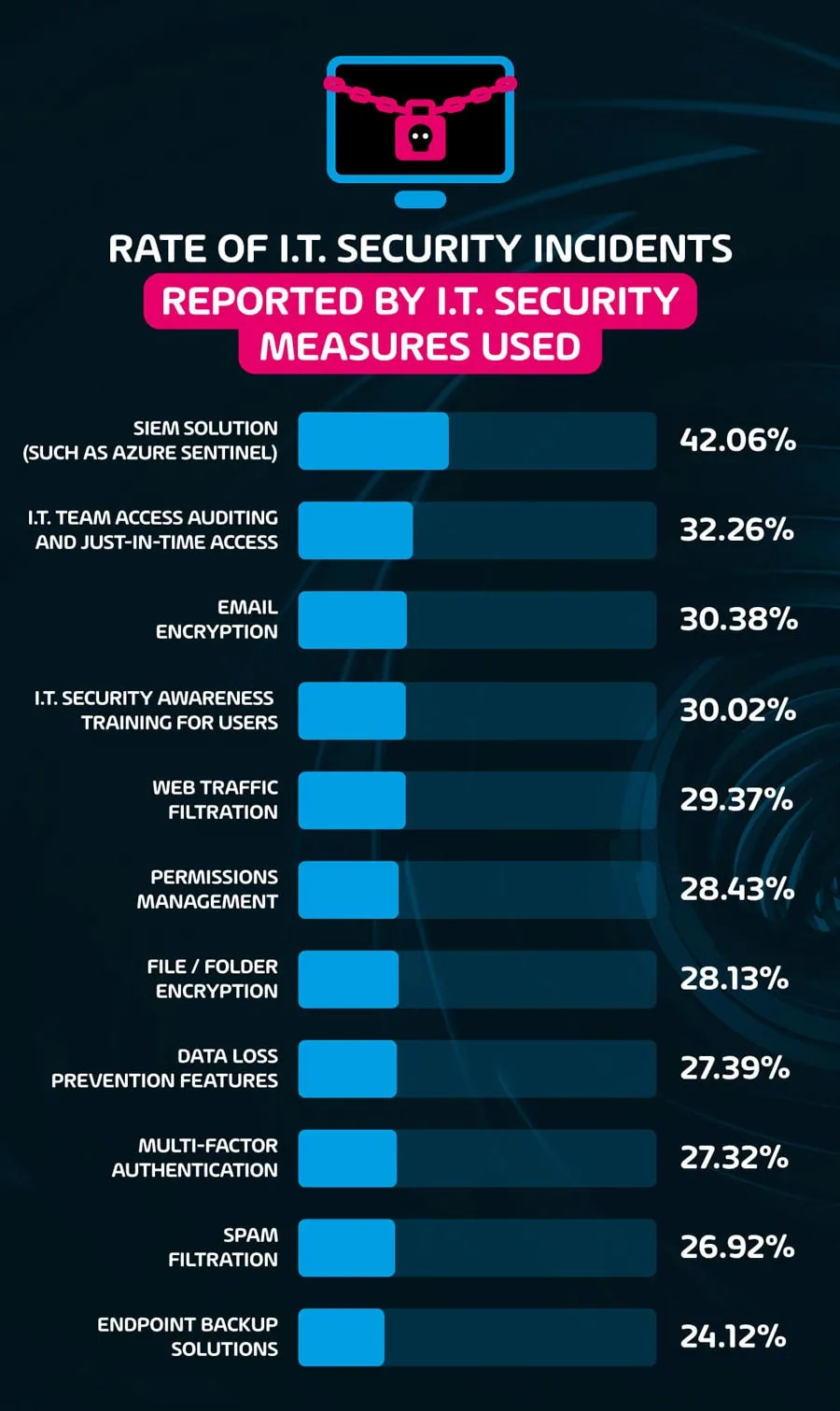
Which security measure corresponds to the lowest amount of IT security incidents?
Among all measures provided, Endpoint Backup solutions corresponded with the lowest rate of incidents reported by respondents. 24.1% of those using this security measure reported an incident in the last year, in comparison to 42.1% of those using SIEM solutions – the highest among the measures provided. While this doesn’t mean that using Endpoint Backup solutions will reduce the rate at which incidents within organizations occur, it does indicate that those organizations that allocate resources to this measure seem to be less at risk.
This data also indicates that while SIEM solutions such as Azure Sentinel can provide real time analytics to combat security threats, it cannot be relied upon to do so on its own. The high rate of security incidents reported by those that use this solution indicates that the presence of an SIEM solution may instill a false sense of security, and lead to less active monitoring by members of the IT department.
Only 28.4% of organizations say IT spend is driven by top security concerns ‘most’ or ‘all’ of the time
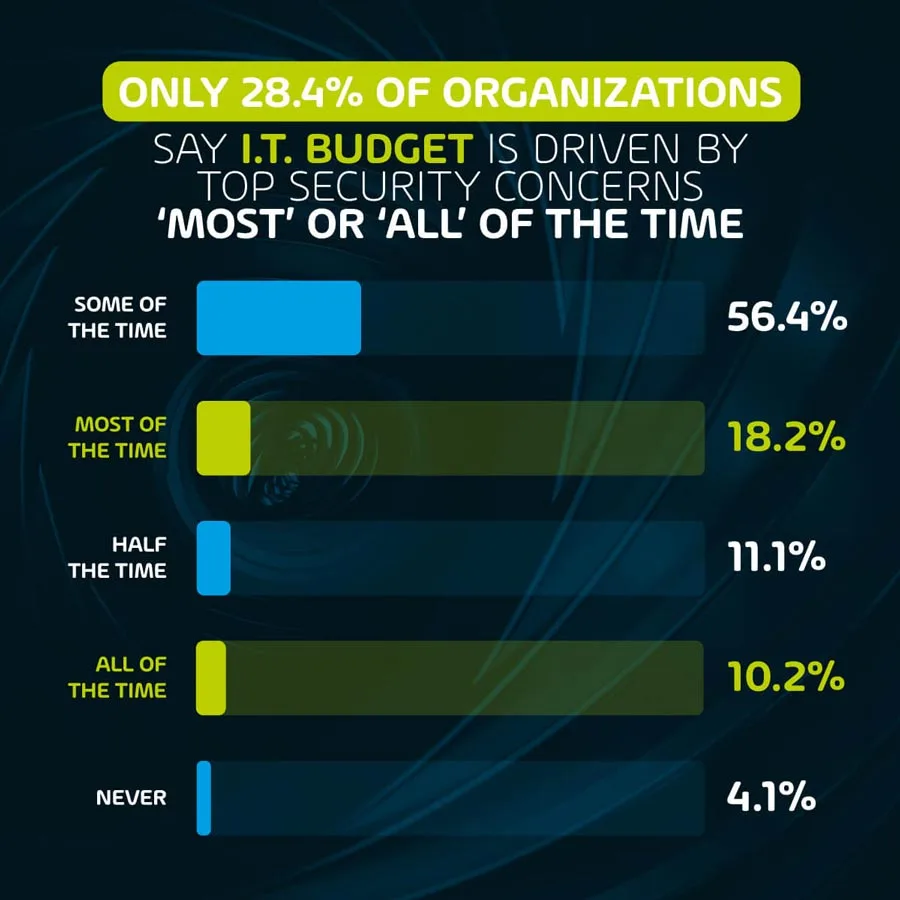
Considering that digital security should be one of the top priorities for any organization from an IT perspective, we’re quite surprised by the lower number of organizations where security concerns drive IT spend consistently. Interestingly, over half of all respondents (56.4%) reported that security concerns drive IT spend only ‘some of the time’.
When asked about the main roadblocks to implementing security features within their organization, almost 2 in 3 respondents (62.6%) cited ‘not enough time or resources’, 44.6% cited a ‘lack of budget’, and 36.2% pointed towards ‘skilling issues and/or lack of knowledge’. Nearly 1 in 4 respondents (23.1%) also mentioned a ‘lack of interest from management’.
These results seem to indicate that even while 1 in 4 organizations are targeted by security threats, this high incidence rate is not reflected in the actions of many companies’ IT spend.
55.5% of organizations do not have a change tracking and review process.
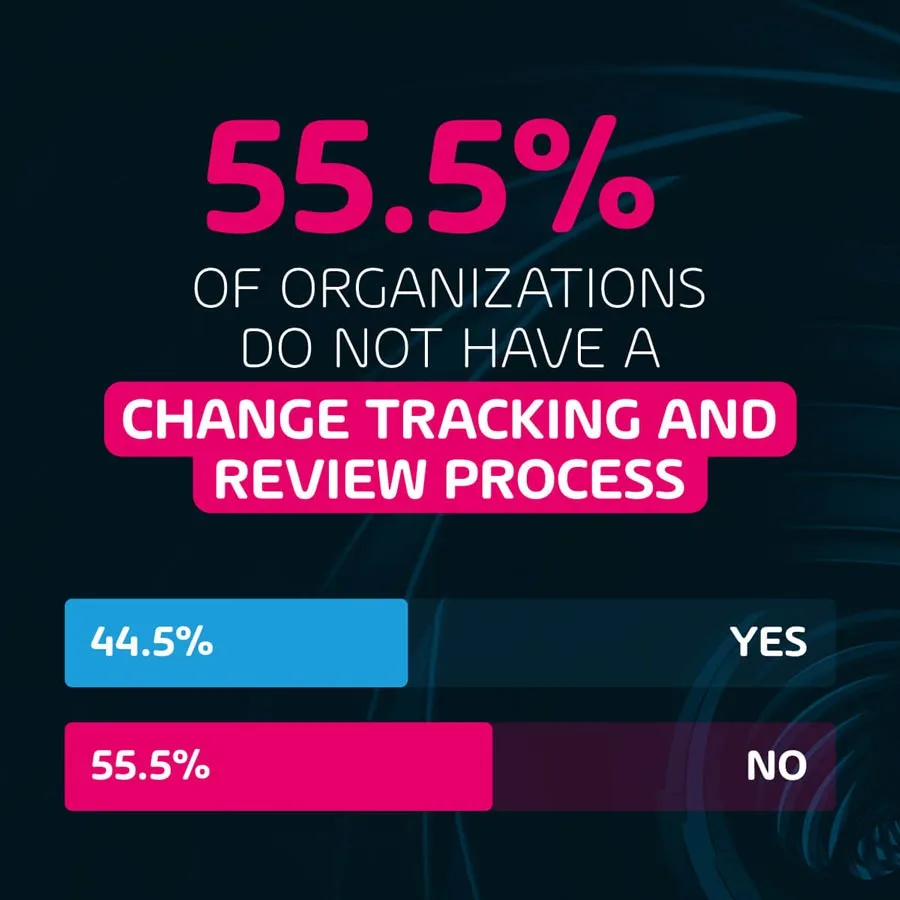
Continuing to illustrate the lack of effort being made by many organizations to stay ahead of security threats, over half of our respondents reported that their organization does not have a change tracking and review process in their IT department. Lack of change control and review can lead to increased data security risks and breakage. A lack of tracking can also make it more difficult to understand where certain security threats are coming from and to pinpoint weak points in the system that require maintenance and added security.
Nearly 2 in 3 (63.5%) organizations are subject to regulatory requirements
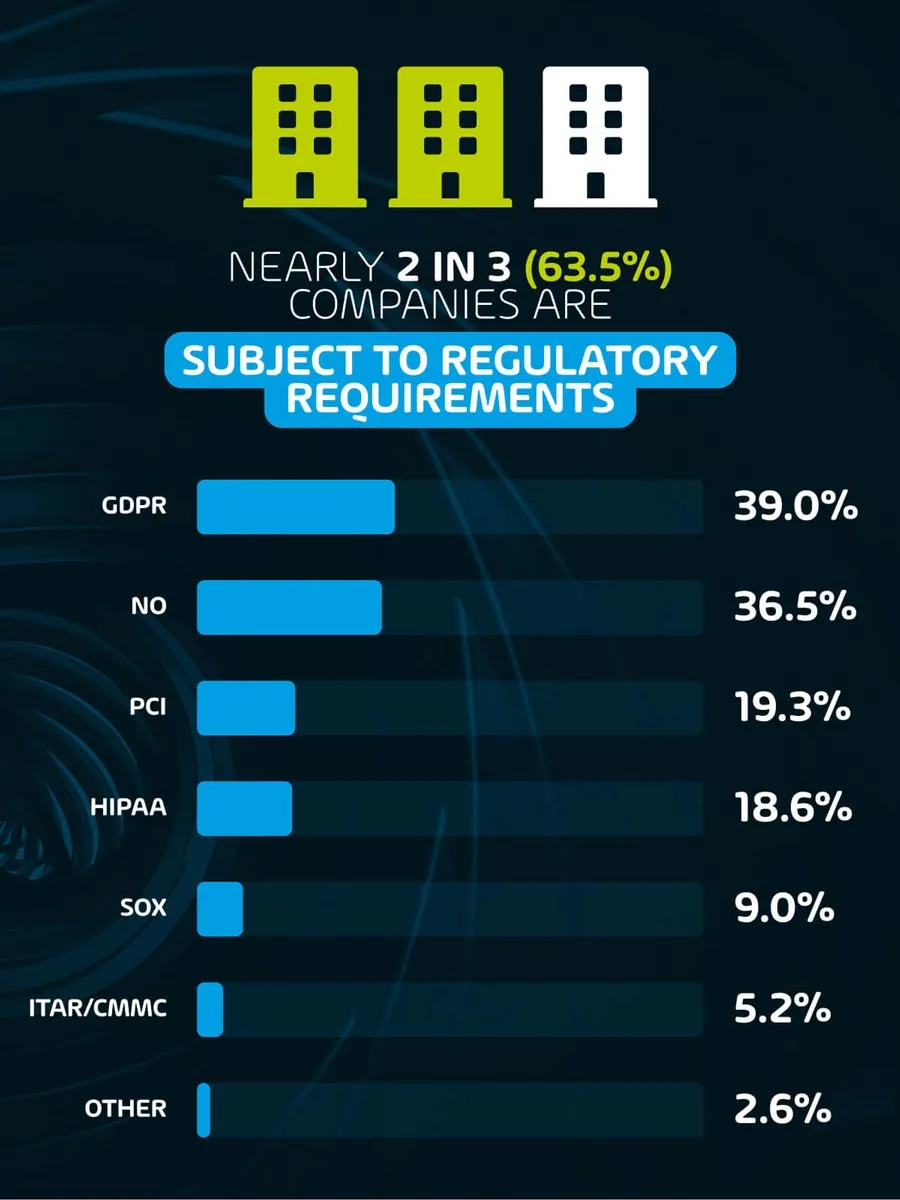
The most common regulatory requirement found through the survey is GDPR, relating to 39% of all respondents. Two other regulatory requirements that are almost equally common are PCI (19.3%) and HIPAA (18.6%). Over half (52.8%) of respondents reported that these compliance requirements drive IT spend only ‘some of the time’, with just 26% reporting that IT spend is driven by compliance ‘most’ or ‘all’ of the time.
7 in 10 (70.5%) organizations invest in IT security beyond regulatory requirements

Despite IT budgets not always being affected by regulatory requirements, according to our survey, over 7 in 10 organizations invest in IT security beyond what is required by compliance regulations. Still, the inverse is also true, with 3 in 10 companies investing just enough in their IT security to meet requirements. The reasons cited by survey respondents as to what the main roadblock to implementing compliance needs include ‘not enough time or resources’ (65.1%), ‘lack of budget’ (40.1%), ‘skilling issues and/or lack of knowledge’ (38.7%) and ‘lack of interest from management (20%).
Full IT security & compliance survey results
If you’d like to look at the data for yourself, you can review the IT Security Compliance survey results here.
About the IT security & compliance survey respondents
Here’s a full breakdown of the survey respondents , for full context relating to the data above.
In terms of the way IT is handled within the surveyed organizations, there are three main subsets. 37.3% of respondents provide IT Managed Services, 31.4% use only internal IT resources, and 21.8% use the services of a Managed Service Provider (MSP), IT Consultant, or Value Added Reseller. The remaining 9.5% of respondents either have a single individual responsible for IT (but it’s not their primary role or they use a shared IT resource).

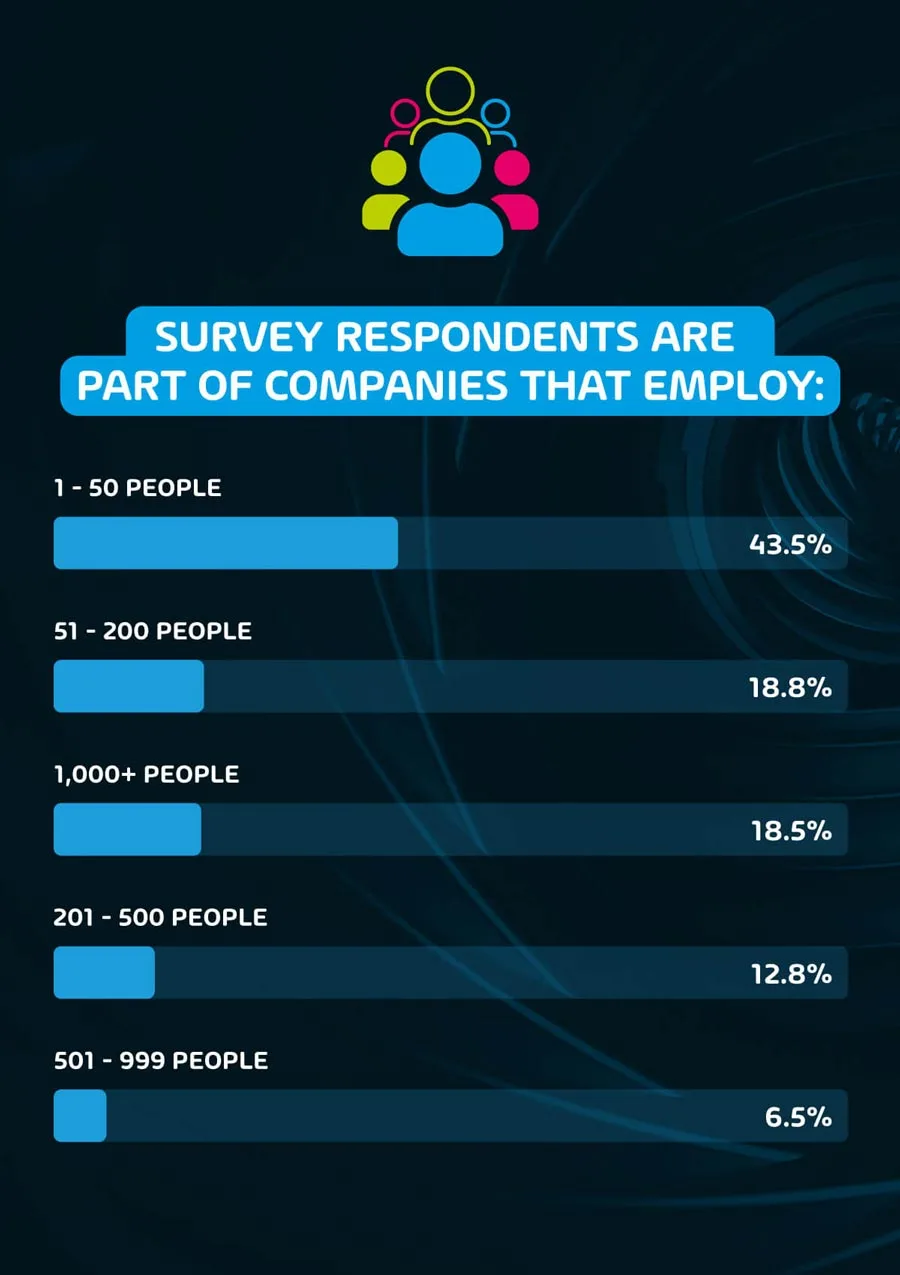
The size of the businesses (by employee count) that our respondents form part of varied between 1-50 (43.5%), 51-200 (18.8%), 201-500 (12.8%), 501-999 (6.5%), and 1,000+ (18.5%).
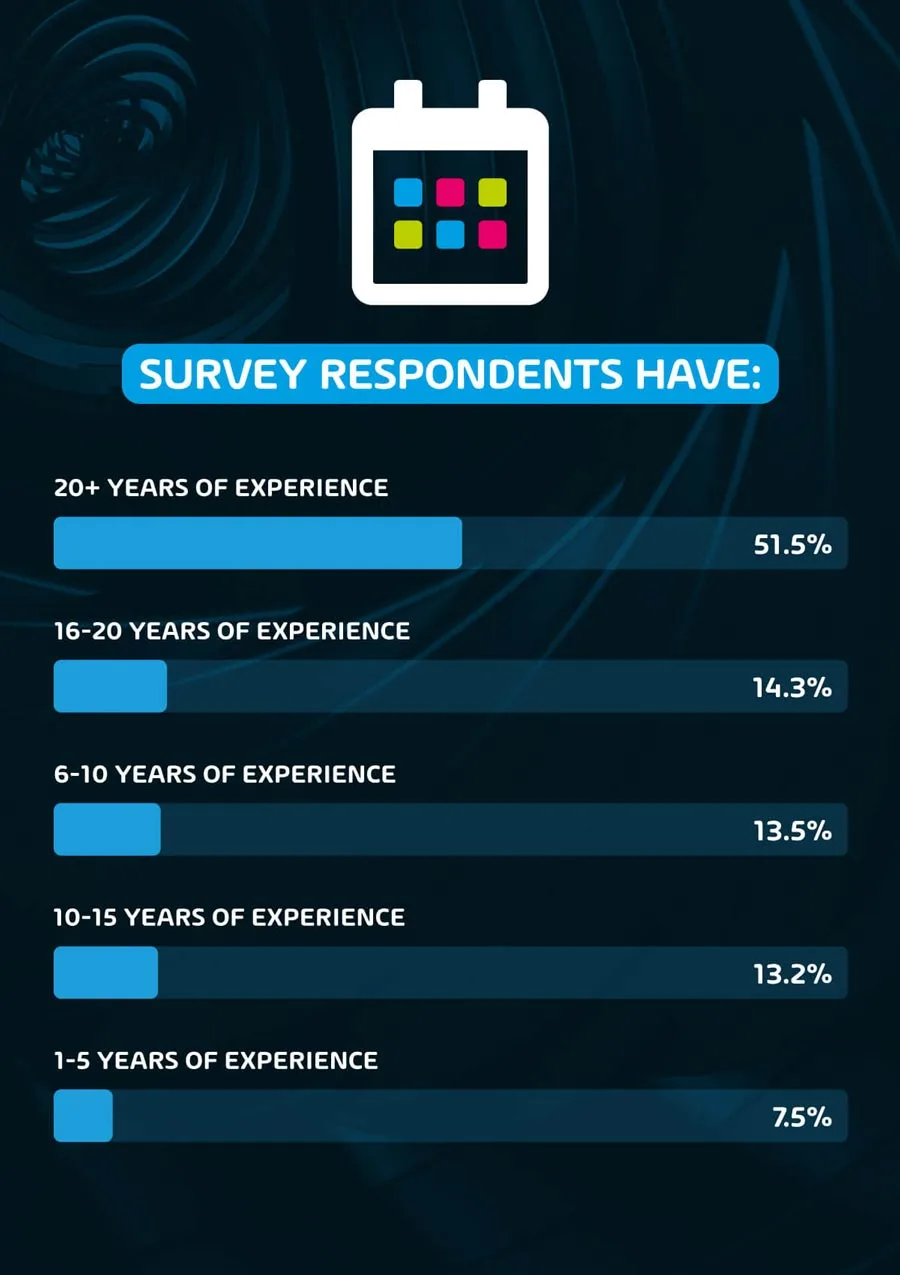
We also asked our respondents how many years of experience they have in the IT industry. Over half (51.5%) reported over 20 years of experience in the field. The rest are split between 16-20 years (14.3%), 10-15 years (13.2%), 6-10 years (13.5%) and 1-5 years (7.5%).
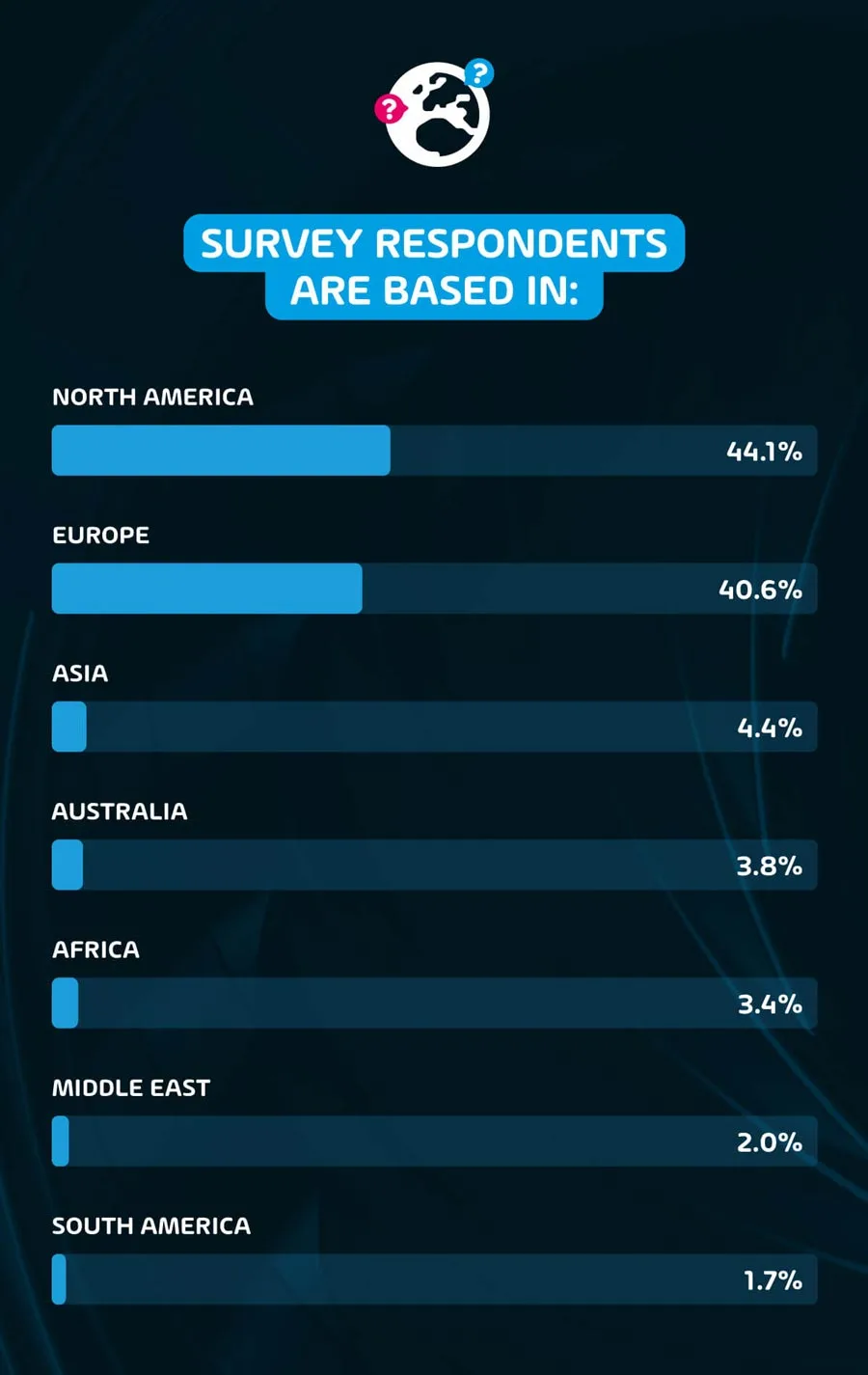
In terms of geography, the vast majority of respondents are based in North America (44.1%) and Europe (40.6%). Meanwhile, the remaining 14% are split between Asian territories (4.4%), Africa (3.4%), Australia (3.8%), the Middle East (2%) and South America (1.7%).
Conclusion
Keeping organizations and their clients safe from external threats is one of the chief concerns of IT teams across the world. It’s one of the most complex and fast-moving sectors in the industry, and for good reason. Data breaches and cyber-attacks are practically an industry unto themselves, with successful attacks costing businesses and their clients millions of dollars every year.
As we’ve discovered through these survey results, increasing compliance requirements does not mean the complete negation of any threat. Independent, constant and proactive vigilance by each organization is still essential to provide the best chance of thwarting potential attacks, regardless of the variables involved.
We hope you’ve found the breakdown of the results above insightful, but if you’d like more detailed data, the full IT security compliance survey results are also available.

