

Hornetsecurity Ransomware Attacks Survey: 2023 Edition
6 in 10 respondents are ‘very’ to ‘extremely’ concerned about ransomware attacks impacting their organization, the Hornetsecurity 2023 Ransomware Attacks survey finds.
Key Takeaways from the 2023 Ransomware Attacks Survey by Hornetsecurity
- 93.2% of respondents rank ransomware protection as ‘very’ to ‘extremely’ important in terms of I.T. priorities for their organization.
- 12.2% of respondents do not have a disaster recovery plan in place in the event of a ransomware attack.
- 90.5% of respondents say they protect their backups from ransomware.
- 75% of respondents cited ‘end-point detection software with anti-ransomware capabilities as the most common tool to combat ransomware.
- 19.7% of respondents said their organization had been the victim of a ransomware attack, with the majority, 62.1%, occurring in the past three years.
- 79.3% of ransomware victims reported that they managed to recover the compromised data from a backup.
- 51.7% of respondents mentioned ’email/phishing’ as the main attack vector for ransomware attacks.
- 81% of respondents said their organization provides user training to recognize ransomware attacks, with 95.8% stating the training was ‘useful.’
- 28.9% of Microsoft 365 respondents said they do not have a recovery plan in place in case of a ransomware attack.
About the 2023 Ransomware Attacks Survey
The Hornetsecurity team conducts regular surveys every few months to keep up with the latest cybersecurity trends within the IT industry. This time, the team decided to revisit yet again a particularly important topic – ransomware.
Commenting on the findings, Hornetsecurity CEO Daniel Hofmann, said: “Our annual Ransomware Survey is a timely reminder that ransomware protection is key to ongoing success. Organizations cannot afford to become victims –ongoing security awareness training and multi-layered ransomware protection is critical to ensure there are no insurmountable losses.”
Last year’s ransomware attack survey found that 1 in 4 IT organizations were victims of a ransomware attack. Considering the continually evolving nature of cyber threats, this year, we decided to explore the most common tools to combat ransomware, including end-point detection software, backups, email filtering, security awareness, and more.
Ransomware is a highly dangerous malware that encrypts a victim’s files or entire computer systems, rendering them inaccessible. Cybercriminals demand a ransom from the victim, typically in the form of cryptocurrency, in exchange for the decryption key to unlock the files. Ransomware attacks are designed to extort money from individuals, businesses, or organizations, and they can have severe consequences, including data loss, financial damage, and operational disruption.
Our 150+ survey respondents shared their experiences dealing with ransomware, offering invaluable insights into the most common attack vectors and concerns.
The Evolution of Ransomware
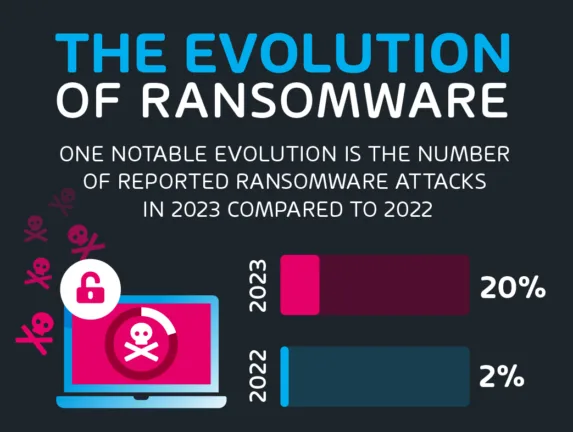
Over the past years, the evolution of ransomware has been nothing short of alarming. As cybercriminals continue to refine their tactics and capitalize on vulnerabilities, the ransomware landscape has evolved into a multifaceted and formidable threat.
One notable evolution is the number of reported attacks in 2023 compared to 2022. In 2022, 20% of our survey respondents reported a ransomware attack in the previous 12 months, compared to only 2% in 2023.
Speaking on the comparative data from both surveys, Hornetsecurity CEO Daniel Hofmann, said: “Although organizations have reported fewer ransomware attacks in 2023, the threats haven’t necessarily decreased,“ Hofmann said. “Cybersecurity awareness among all users remains a crucial element to further decrease the risk of falling for these threats, especially as attacks become more sophisticated with new technologies.”
Another notable evolution is the diversification of attack vectors. If we compare the 2023 survey with last year’s, we see a slight decrease in email and phishing vectors, 6 in 10 in 2022 compared to 5 in 10 in 2023. On the other hand, we see a 5% increase from ‘compromised endpoints’ and a 6% increase from ‘social engineering’ sources. Moreover, ‘zero-day exploits’ see a further 4% increase from the previous year.
Furthermore, the layer of extortion to attacks is another glaring difference in the evolution of ransomware. Compared to previous years, ransomware attacks have adopted a multi-layered approach, which includes threatening to leak sensitive data if the ransom isn’t paid. This ‘double extortion tactic’ has been highly effective, as organizations face not only the prospect of data loss but also reputational damage and regulatory penalties if sensitive information is exposed.
But the evolution of ransomware is best described through the emergence of Ransomware-as-a-Service platforms. These platforms have democratized ransomware attacks, essentially allowing individuals with limited or no technical expertise to launch ransomware campaigns. The RaaS model makes it easier for criminals to launch ransomware attacks across various industries, not just IT and critical infrastructure.
Finally, the data from 2022 and 2023 reveal noteworthy shifts in the most common targets of ransomware attacks. In 2022, server infrastructure and network storage held the unfortunate distinction of being the primary target, with a significant 56% incidence rate. Multiple endpoints and single endpoints closely followed, at 36.6% and 35.3%, respectively. Backup storage was also a notable target, affecting 15.1% of organizations.
However, in 2023, the landscape shifted. Server infrastructure and network storage remained prominent but saw a decrease to 44.8%, while multiple endpoints and single endpoints followed at 34.5% and 31%, respectively. Intriguingly, backup storage attacks dropped to 6.9%, suggesting a shift in cybercriminal tactics towards different targets, possibly due to improved backup security.
Microsoft 365 and cloud data, while still vulnerable, decreased to 3.4%. These changes underscore the dynamic nature of ransomware targeting strategies and the overall evolution of the malware.
The Current Ransomware Landscape
In recent years, the ransomware landscape has evolved into a formidable and pressing concern for organizations worldwide. This malicious software, which locks away critical data until a ransom is paid, has become a pervasive threat with increasingly dire consequences.
One of the key reasons why ransomware has grown into a paramount concern is its adaptability. Cybercriminals continually refine their tactics, targeting both individuals and institutions with impeccable precision. They exploit vulnerabilities in software, employ sophisticated phishing campaigns, and leverage social engineering techniques to gain access to a victim’s systems. This adaptability keeps them one step ahead of security measures and underscores the ever-present danger.
For businesses, the implications of falling victim to a ransomware attack are profound. The most immediate consequence is financial loss. Organizations are forced to weigh the cost of paying the ransom against the value of their encrypted data. Even if the ransom is paid, there is no guarantee that the criminals will provide the decryption key, leaving businesses in a precarious position.
Furthermore, regulatory penalties can compound the financial damage. Many jurisdictions require organizations to disclose ransomware incidents, potentially leading to fines for non-compliance. These penalties are designed to incentivize proactive cybersecurity measures but add to the already substantial financial burden.
Beyond financial implications, ransomware attacks also have significant reputational consequences. Businesses may lose the trust of customers, partners, and investors. Moreover, news of a successful attack can tarnish an organization’s image, erode customer loyalty, and ultimately impact its bottom line.
To combat the growing ransomware threat, businesses are adopting multifaceted strategies. These strategies include robust cybersecurity measures, employee training programs to recognize phishing attempts, and investing in data backup and recovery solutions. Many organizations are also turning to cyber insurance to mitigate the financial risks associated with ransomware attacks.
In this increasingly dangerous landscape, it is paramount that organizations remain vigilant and proactive in safeguarding their data and systems. As cybercriminals continue to adapt and ransomware attacks grow in sophistication, the stakes have never been higher. Mitigating the risks and consequences of ransomware requires a holistic approach, combining technology, education, and preparedness to remain one step ahead in the ongoing battle against this pervasive threat.
6 in 10 Respondents Are ‘Very’ to ‘Extremely’ Concerned About Ransomware Attacks

The survey uncovers a notable level of concern within organizations regarding the potential impact of ransomware attacks. Among the respondents, a significant majority, comprising 32.7%, express a ‘very concerned’ sentiment.
This heightened level of concern likely stems from the growing frequency and advanced sophistication of ransomware attacks, which have been known to cripple organizations, disrupt operations, and lead to financial losses. Furthermore, an additional 26.5% of respondents fall into the ‘extremely concerned’ category, indicating that ransomware is viewed as a substantial and imminent threat.
While a substantial portion is highly concerned, the survey data also reveals a range of sentiments. About 21.1% of respondents feel ‘moderately concerned,‘ suggesting a more tempered but still significant level of worry. Another 19% express being ‘slightly concerned,’ indicating a degree of awareness but perhaps less urgency in their perception of the threat. Interestingly, only a minute 0.7% indicate they are ‘not concerned at all.’
This outlier response could be attributed to the relatively low awareness of ransomware’s potential impact, overconfidence in existing security measures, or a misunderstanding of the risks involved.
1 in 10 Respondents Have No Disaster Recovery Plan in Place in Case of Ransomware Attack

The data reveals a critical aspect of organizational preparedness in the face of ransomware attacks. Surprisingly, a significant majority, 87.8%, reported having a disaster recovery plan to counteract the potential fallout from a potential ransomware attack.
This high percentage reflects an awareness within these organizations of the necessity for proactive measures to mitigate the impact of ransomware incidents. A well-structured disaster recovery plan is essential in ensuring critical data can be restored swiftly and efficiently, minimizing downtime and potential financial losses.
On the other hand, the 12.2% of organizations that admitted to lacking a disaster recovery plan are in a more precarious position. Among this group, it’s striking to note that over half (55.6%) attributed their lack of preparedness to resource constraints or time limitations. This suggests that for some organizations, the challenge lies in allocating the necessary resources, both in terms of personnel and financial investment, to develop and maintain a comprehensive disaster recovery plan.
Additionally, it’s concerning that 33.3% of those without a plan mentioned that disaster recovery planning isn’t considered a priority by management. This highlights the need for organizations to recognize the importance of such plans and foster a culture of cybersecurity awareness and readiness at all levels of decision-making.
The findings highlight the divide between organizations that have embraced preparedness and those that may be exposed to greater vulnerabilities due to resource constraints or a lack of prioritization, albeit one side is heavily skewed compared to the other.
Less Than 1 in 10 Respondents Don’t Protect Backups From Ransomware
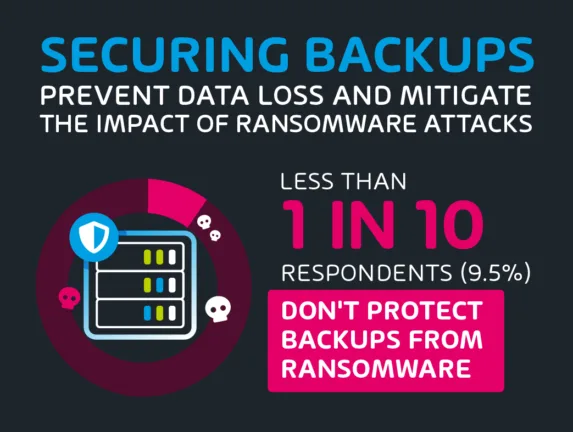
The data reveals valuable insights into how organizations safeguard their backups against ransomware threats. Among the respondents, a substantial majority (90.5%) indicate they currently protect their backups from ransomware. This high percentage underscores the growing awareness of the importance of securing backups to prevent data loss and mitigate the impact of ransomware attacks.
Regarding the primary security features used for backup protection, the most prevalent choice is ‘immutable storage,’ selected by 40.6% of respondents. This approach ensures that once data is stored, it cannot be altered or deleted, providing a robust defense against ransomware encryption.
‘Tight control of user and application permissions’ follows closely, chosen by 38.3% of respondents, emphasizing the significance of controlling access to prevent unauthorized changes. ‘Air-gapped storage’ is another favored method, selected by 27.8% of respondents, reflecting the practice of physically isolating backups from the network to thwart ransomware attacks.
Moreover, when it comes to confidence levels in their chosen backup protection methods, the majority express high confidence. Approximately 43.6% are ‘very confident,’ and 39.8% are ‘moderately confident.’ This confidence suggests that organizations diligently evaluate and implement robust security measures to fortify their backup systems against the ever-present ransomware threat.
Finally, 76.2% of respondents said the threat of ransomware attacks changed the way their organizations backup data. This highlights a fascinating finding. Namely, the high-profile nature of ransomware attacks has forced businesses to rethink their data backup strategies and implement stricter security measures that protect data while in transit and at rest.
9 in 10 Respondents Cited ‘End-Point Detection Software With Anti-ransomware Capabilities’ as the Tool Used to Combat Ransomware

Next up, the survey asked respondents to select the tools they use to combat ransomware threats. Surprisingly, the survey finds that organizations utilize a wide range of security tools to fortify their defenses.
Most notably, 75% of organizations have adopted end-point detection software with anti-ransomware capabilities as a crucial defense against ransomware attacks. Email filtration and threat analysis are also widely embraced, with 68.8% of organizations employing this protective measure, recognizing the importance of scrutinizing incoming emails for potential threats.
Security Awareness Services, chosen by 51.8% of respondents, demonstrate a growing emphasis on educating employees about ransomware risks. Immutable storage, selected by 47.3%, is an effective strategy for safeguarding critical data, making it unalterable and resilient to ransomware attacks. Implementing air-gapped storage (27.7%) shows a commitment to isolating critical data from online threats.
AI-enabled Security Solutions (22.3%) and application whitelisting (21.4%) indicate a shift towards advanced technologies to combat ransomware. Notably, only 1.8% of respondents reported no security features.
Finally, a small percentage (0.9%) mentioned ‘Other’ measures, pointing out the diverse and evolving strategies organizations employ to mitigate the ransomware threat. These responses collectively underline the multifaceted approach organizations are taking to protect their digital assets against the growing menace of ransomware.
2 in 10 Respondents Said Their Organization Had Been the Victim of a Ransomware Attack

The data highlights a crucial aspect of the ransomware landscape, revealing the experiences of organizations with these malicious attacks.
It’s encouraging to note that a majority, 80.3%, of the surveyed organizations have not fallen victim to a ransomware attack. However, what stands out is the persistence of ransomware incidents over time. Approximately 19.7% of organizations have experienced an attack at some point in their recent history. Interestingly, a significant portion of these incidents occurred more than three years ago, as indicated by 12.2% of respondents.
This suggests that some organizations may have learned from past experiences and bolstered their defenses, reducing their susceptibility to ransomware in the short term. Nonetheless, the fact that a smaller percentage reported incidents within the past year (2% in the last 12 months) highlights that ransomware remains a dynamic and persistent threat, necessitating ongoing vigilance and cybersecurity measures to mitigate the risk of falling victim to these disruptive attacks.
8 in 10 Ransomware Victims Reported That They Managed to Recover the Compromised Data From a Backup

In the survey data, we can see insights into the aftermath of ransomware attacks and the various responses organizations have had to such incidents. Among the respondents who answered the question about recovery, a majority (79.3%) reported successfully recovering their data from backups, indicating once again the importance of having a robust data backup and recovery system in place.
However, the data also highlights the significant impact of ransomware attacks, as 17.2% of respondents suffered a partial loss of affected data, and 6.9% were forced to pay a ransom to recover their data. Fortunately, no respondents reported losing all affected data entirely.
Regarding the cost of the ransom paid, it’s notable that 37.9% of respondents preferred not to disclose this information, highlighting the sensitivity and confidentiality surrounding ransom payments. The remaining 62.1% likely represents organizations that did disclose the ransom amount, which can vary widely and often involve significant financial implications.
Additionally, the data sheds light on the targets of ransomware attacks. Server infrastructure and network storage were the primary targets, with 44.8% of respondents affected, followed closely by multiple endpoints (34.5%) and single endpoints (31%). Interestingly, backup storage was the least common target at 6.9%, suggesting that organizations are making efforts to safeguard their backup systems.
Overall, this data underscores the multifaceted challenges posed by ransomware attacks, emphasizing the importance of preventive measures, robust backup strategies, and the need for organizations to remain vigilant in the face of evolving cyber threats.
5 in 10 Respondents Mentioned ‘Email/Phishing’ as the Main Attack Vector for Ransomware Attacks

When examining the data on the vectors of ransomware attacks, a clear pattern emerges. Among the respondents who provided insights into the attack vector, ‘Email / Phishing attack’ stands out as the most prevalent, with 51.7% of respondents citing it as the method by which ransomware infiltrated their systems.
This aligns with the well-established trend of cybercriminals exploiting email vulnerabilities and using phishing tactics to deceive unsuspecting users.
Following closely behind is the ‘Compromised endpoint‘ vector, reported by 20.7% of respondents. This highlights the importance of securing individual devices within an organization’s network, as compromised endpoints serve as gateways for ransomware attacks.
‘Social engineering’ and ‘Unknown‘ vectors each garnered 13.8% of responses, emphasizing the human element in cybersecurity threats. Social engineering relies on manipulating individuals into revealing sensitive information, while the ‘Unknown’ category underscores the challenges organizations face in pinpointing the exact entry point of attacks.
‘Exploit (zero-day or other)‘ and ‘Poor perimeter security’ each received 10.3% of responses, underscoring the significance of keeping software and systems up-to-date and maintaining strong network defenses.
Finally, ‘Other’ factors into the equation with a 3.4% response rate, representing less common but still noteworthy attack vectors. This comprehensive breakdown of attack vectors underscores the need for organizations to implement multi-layered security strategies, including employee training, robust email filtering, and up-to-date software patching, to mitigate the diverse threats posed by ransomware attacks.
8 in 10 Respondents Said Their Organization Provides User Training to Recognize Ransomware Attacks

The data sheds light on the effectiveness of employee training programs within organizations. A significant majority, 81%, offer training to their end users, indicating a widespread recognition of the importance of educating employees about ransomware threats.
Moreover, an overwhelmingly positive response emerges when assessing the perceived usefulness of this training, with 95.8% affirming its value. This high level of endorsement underscores the belief that training empowers employees to recognize and respond effectively to potential ransomware attacks.
However, it’s noteworthy that a portion of respondents (19%) do not provide such training, which suggests that there is still room for improvement in terms of cybersecurity awareness training and preparedness.
When delving into the reasons why some perceive the training as not useful, several factors come to the forefront. Among these, the perception of it being “too time-consuming for end-users” (28.4%) and the belief that “users are untrainable” (18.6%) are common. Additionally, concerns related to cost (13.7%) and the impact on IT staff’s time (13.7%) are voiced. The variety of reasons cited in the “Other” category (40.2%) highlights the multifaceted challenges organizations face when implementing effective anti-ransomware training programs.
While the majority of respondents acknowledge the value of ransomware training, there is a need for tailored approaches that address concerns like time constraints and cost while ensuring that all employees, including those considered “untrainable,” can contribute to a more resilient defense against ransomware threats.
3 in 10 of Microsoft 365 Respondents Said They Do Not Have a Recovery Plan in Place

The survey reveals crucial insights into the preparedness of organizations when it comes to safeguarding their Microsoft 365 data from ransomware attacks. A substantial majority, 84.4%, express concern about the potential impact of ransomware on their Microsoft 365 data, highlighting a widespread awareness of this specific threat. Interestingly, 13.6% admit uncertainty, emphasizing the need for education and awareness campaigns regarding the vulnerabilities of cloud-based data.
The existence of a recovery plan in the event of a ransomware attack is a critical factor, and here, 61.9% claim to have one in place. This demonstrates a proactive approach among a significant portion of respondents. Conversely, 25.2% admit to lacking any sort of recovery plan, leaving their organizations vulnerable to data loss and extortion.
It’s also noteworthy that a sizable proportion (12.9%) does not use Microsoft 365, indicating a diversity of software solutions employed by organizations. Among those with recovery plans, 92.3% rely on third-party backup and recovery solutions, while a smaller portion (26.4%) solely trust Microsoft 365 Retention Policies.
This dual approach suggests that organizations might not trust Microsoft 365’s native security features to protect their cloud-based data sufficiently. The presence of a few respondents opting for ‘Other’ recovery methods (2.2%) underscores the customization of strategies based on specific organizational needs. Overall, the data highlights the importance of proactive planning and a multi-pronged approach to safeguarding Microsoft 365 data from ransomware threats.
About the 2023 Hornetsecurity Ransomware Attacks Survey Respondents
Our survey provides valuable insights into the demographics of IT professional participants. Firstly, it reveals that a significant portion of respondents, 42.9%, have accumulated 21 or more years of experience in the IT industry. This reflects a substantial level of expertise among participants, suggesting a seasoned workforce that may be well-equipped to handle complex cybersecurity challenges.
Regarding geographical distribution, the majority, 46.9%, are based in Europe, followed by North America at 30.6%. These figures align with the global prominence of these regions in terms of technological advancements and IT infrastructure. Notably, the Middle East, with 13.6%, also makes a substantial representation, showcasing the growing significance of this region in the IT landscape.
In terms of business size, a significant majority, 67.3%, come from small to mid-sized organizations with 1-50 employees. This is a common trend, as smaller businesses often comprise a substantial portion of the IT market. However, it’s worth noting that 6.8% of respondents hail from larger enterprises with 1,000 or more employees, indicating a diverse mix of organizational sizes participating in the survey.
Overall, the data paints a picture of experienced IT professionals primarily based in Europe and North America, representing a range of business sizes. This diversity among survey participants provides a well-rounded perspective on the ransomware landscape, taking into account the experiences and contexts of IT professionals from various backgrounds and regions.

