Protect Yourself from Malicious Email Attachments with These Expert Tips
Email is core to modern business communications. In most organizations internal messages are often sent via Microsoft Teams, Slack or similar instant messaging apps, but when it comes to communications between businesses, email is still king.
That makes email very attractive for criminals, and email borne attacks of all flavors are still the main way attackers compromise your businesses.
There are several types of malicious emails, such as phishing (tricking you to click a link leading to a dangerous website), Business Email Compromise (BEC, conning you into transferring money to a different account number for an invoice) and file attachments.
These look like a normal Word, Excel, image or PDF file that we’re all accustomed to receiving, and when opened, may even look like benign file. But hidden inside is some sort of malicious payload, infecting your device, or even your business network.
This article focuses on these malicious email attachments, what the risks are, how to train your users to spot them, how you can protect your business, the different types of malware attachments and ultimately how you can best keep them out of your user’s inboxes in the first place.
Why Malicious Email Attachments Are So Dangerous
Most of us receive files attached to emails as part of our daily work life, and it’s natural to open them to perform whatever the next step is in the business process: read the information, edit the draft, fill in the PDF form or update the spreadsheet with the latest figures.
This is why they’re so “popular” amongst criminals, anytime they can insert themselves into a normal process, they’re much more likely to fool their victims.
There are different types of malware attachments, both the file type and the attack type. Let’s start with the attack type where some simply have the malware embedded in the file. This could be a virus, or even a ransomware payload that’ll try to encrypt all documents on your local device, and perhaps on file shares you have access to as well and then demand payment for the decryption key.
This type of ransomware is rare today, firstly because they’re easy to spot for email hygiene solutions such as Hornetsecurity’s Advanced Threat Protection which will open every incoming email attachment file in a sandbox and inspect its actions and if they’re malicious the email will never even reach the user’s inbox.
And secondly, even if the email hygiene solution misses the malware, when it tries to execute on the device, the Endpoint Detection and Response (EDR) is likely to block it. It’s also partially because this type of ransomware (and malware in general) is very imprecise as the attackers don’t know which of the thousands of emails they send out is going to lead to a successful breach.
Incidentally, these types of malware attacks were popular over a decade ago, before the criminals had perfected the model of ransoming your entire business network.
Today, the attached malware is much more likely to be aimed at stealing identities. A popular approach is a PDF that needs to be digitally signed for example and then links to an Attacker in the Middle (AitM) webpage where the user must sign in to their account (where the criminals steal your credentials in the background, unbeknownst to the user).
Another type of malware is infostealers, a small application that’ll run silently in the background on your device, copying all passwords and other secrets that you enter on any site to the criminal’s servers.
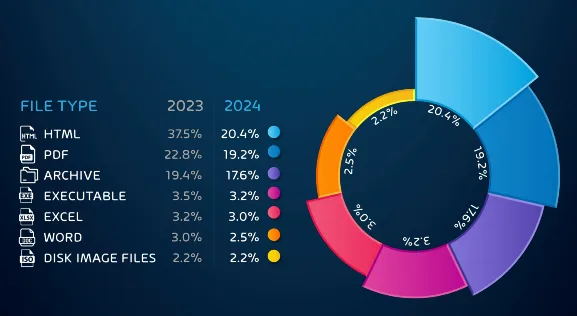
As you can see in the diagram, HTML files are the most used which makes sense as they render easily both on computers and smartphones, plus they can be crafted to look like almost anything. PDF files are in second place, it’s very normal to receive PDF files and interact with them, plus they can be weaponized in several different ways.
The use of archive files (ZIP, RAR etc.) is a way to evade detection. Often the attackers will password protect the file and send the password to the user via a different channel. Email hygiene solutions can’t access the archive file to inspect the file(s) inside it if it’s password protected, making it less likely that the email will be blocked before reaching the user.
Compared to a few years ago, Excel and Word files have shrunk dramatically in popularity, based on Microsoft blocking active content in Office by default, but we still see these attachments, combined with an enticing reason for the user to activate the macro / embedded malicious code. Another notable trend from the Report is the overall decrease in malicious attachments as attackers pivot to other attack types.
Sometimes the attachment doesn’t contain the malicious payload and instead the attackers attempt to bypass email filters by having a perfectly safe PDF or HTML file, with a link to a site where the attack comes from.
And many email attacks blend different attack types together for improved chance of success, such as making a Business Email Compromise (BEC) scam work better with an attached PDF invoice (no malicious content), and the attack is actually the text in the phishing email that looks like it’s coming from your superior asking you to pay the attached invoice quickly.
The main reason for most phishing emails today, with or without a malicious attachment, is to compromise a user’s account and / or device. Once this beachhead is established by the criminals they’ll then pivot internally in your network to other devices.
In some cases, they’ll use a compromised mailbox to send phishing emails internally to further compromise other users and devices, in other cases they’ll compromise servers with the aim of gaining complete control of your internal system.
This is how modern ransomware attacks work (unlike the single ransomware attachment described above) where criminals (hands on keyboards / Human Operated) gain full dominance of your internal domain, wipe your backups if they can, and exfiltrate your sensitive data before running the ransomware attacks across all systems at once.
This means extensive work is required to rebuild systems, especially if you can’t trust or access your data backups if your business doesn’t pay the ransom, plus the threat of the criminals dumping your sensitive data publicly that they copied first, if you don’t pay (double extortion). And it often started with a single malicious email slipping through your defenses.
The Rise of AI-Driven Phishing and Malware Attacks
The rise of Generative AI to create images and text content is a boon to business productivity, but like any tool is used by attackers as well.
We’ve seen malware developers use AI coding assistants to improve their code (just like any developers do) and create custom versions for each intended victim, further increasing the chance that it’ll bypass defences.
The main way AI is helping attackers is by fine tuning phishing email text. Gone are the grammar and spelling mistakes of yesteryear, and email wording is often fine-tuned for each victim organization. Another way GenAI is helping criminals is by translation to other languages.
Crafting a successful attack against targets in a country where you’re not a native speaker of the language is difficult but excellent translations are now but a prompt away, bringing phishing to many more countries in the world.
Essential Features to Combat Malicious Email Attachments
There are two components to keeping your organization and your users safe from malicious emails and attachments. The first is ensuring that as few as possible of them reach users inboxes, but as no cyber security product is 100% effective all the time, the second is to train your users to be aware and tuned to the signs of maliciousness.
Our industry leading email hygiene solution, Advanced Threat Protection applies defence in depth to the problem of email security, applying multiple steps to identify benign emails and malicious ones. Start by getting your basic email policies in place, with SPF, DMARC and DKIM settings, our DMARC Manager makes this process easy.
Then we use spam and malware detection for all incoming and outgoing emails to catch the “low hanging fruit” with a guaranteed 99.9% detection of spam, and 99.99% for viruses.
Advanced Threat Protection (ATP) then scans all links in emails to ensure they’re safe before letting the email through. This is followed by “time of click” protection as well, because a popular attack is to compromise a website (the target of the links the attackers put in the emails) but not actually activate the malicious payload until after the emails have been delivered.
With “time of click”, even if you click the link a day later, our Secure Links feature will block your access if the target of the web link is now malicious. ATP will also identify QR codes that lead to malicious content and block these emails are well.
Attached files are opened in a sandbox and the resulting activity of the file is inspected, again ensuring that malicious attachments are blocked before they even show up in your user’s inboxes. If the attachments are encrypted our engines decrypt them before running a full scan.
The whole protection stack is rounded out by Real-Time Alerts and Comprehensive Reporting so you know what’s going on and can take action against targeted email attacks, plus report to leadership how well your protection is working.
Best of all, Hornetsecurity’s email protection is easy to set up, with both an API based access option and a DNS record option, providing easy onboarding and the ability to try it out without making major changes to your infrastructure.
This best-in-class email hygiene solution needs to be combined with training your users, they’re your last line of defense for any malicious phishing email or attachment that slips through all the other layers of defense.
Our Security Awareness Service is AI based, building up profiles of each user and sending simulated phishing emails on a regular basis, but adapting the difficulty and frequency (automatically, no admin time involved) based on each user’s behavior. And instead of infrequent, long, training sessions that no one remembers a few weeks later, small, targeted, engaging video trainings improve user awareness over time.
Protect Your Inbox from Malicious Attachments with Hornetsecurity
Don’t leave your organization vulnerable to sophisticated cyber threats. With Hornetsecurity’s Advanced Threat Protection and Spam & Malware Protection, you’ll stay one step ahead of attackers and ensure your email security is ironclad.
Request a demo today to see how we can help secure your organization against malicious email attachments.

Conclusion
Malicious email attachments pose a serious threat to businesses, putting sensitive data and operations at constant risk. To stay secure, advanced solutions are essential, and Hornetsecurity’s Advanced Threat Protection, combined with Spam & Malware Protection, offers comprehensive tools that effectively guard inboxes against even the most sophisticated attacks.
By choosing these protections, businesses can take control of their email security, prevent costly breaches, and keep valuable data safe. Now is the time to explore how Hornetsecurity’s powerful defenses can strengthen your organization’s cybersecurity.
FAQ
The important thing to look for, whether the email is from a known contact (remember, their account might have been compromised) or someone new is the signals of the wording and requested action. If it’s trying to make you feel emotional (“you’ve won a prize”, “unlock your account now or lose access”), that’s a red flag, as is any time pressure. Both tactics are designed to short circuit your suspicious mind and make you act before you’ve really thought it through. When in doubt, don’t take the requested action, or open the attachment(s) and instead contact your IT / security department.
Please contact your IT / Security department straight away and tell them the steps you took. It’s a natural human reaction to try to hide what you’ve done once you realize that it might have been dangerous, but this only worsens the situation, whereas letting the defenders know as soon as possible allows them to investigate and possibly prevent a small breach turning into something more serious.
Training your team to identify and handle malicious email attachments is vital in bolstering your organization’s cybersecurity. Start by conducting regular, engaging training sessions that focus on the types of malicious attachments and the tactics used by cybercriminals. Use real-world examples and scenarios to illustrate the potential risks. Implement a comprehensive security awareness program that includes simulated phishing campaigns; this allows employees to practice identifying threats in a safe environment.