

Email Security Trends and Attack Techniques in Microsoft 365
Email remains a cornerstone of business communication, and thus is also continues to be a primary vector for cyber-attacks. Despite the rise of collaboration tools like Microsoft Teams, email’s ubiquity makes it a prime target for threat actors.
On an annual basis, Hornetsecurity’s dedicated Security Lab reviews the company’s extensive data set and analyzes the state of global email threats and communication statistics. Additionally, the team regularly conducts forward-thinking exercises and provides insight into potential future threats. This article focuses on reviewing data points from during the defined data period Nov 1st 2023 to Oct 31st 2024, which forms the basis for projections of the changing threat landscape laid out in our Cybersecurity Report.
Email Security Trends
Despite increasing usage of collaboration and instant messaging software, such as Microsoft Teams, email continues to be a top area of concern in terms of cyberattacks. We’ve observed a continued decrease in the number of emails categorized as Threats/AdvThreats – 2.3% this year, compared to 3.7% from last year, and 5.5% the year before that (When looking at “Unwanted” emails).
That said, the risk to businesses around the globe remains high. This is primarily due to increased use in social engineering techniques via low-effort spray-style email attacks that seek to get the target user to engage somehow.
By reviewing more than 55.6 billion emails collected over the current reporting period (1 November 2023 – 31 October 2024), the Security Lab has made the following determinations:
Spam, malware, advanced threat metrics
As we’ve seen over the last decade, email continues to be one of the primary methods that threat actors use to launch attacks. Our data from this report’s data period classifies 36.9% of all emails as “Unwanted” – a 0.6 percentage point increase from 2023.
The definition of “unwanted” refers to emails that are not genuine communications desired by the recipient. The chart below shows our breakdown of unwanted emails along with clean emails.
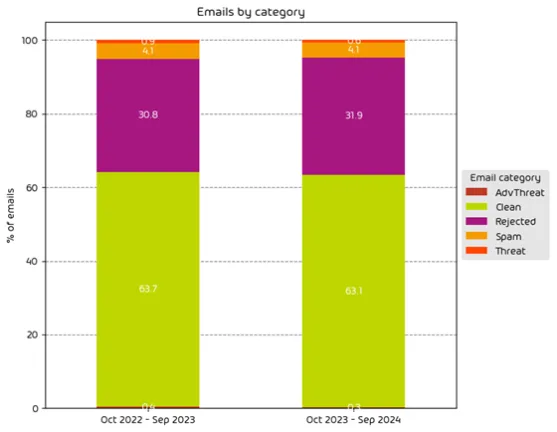
2024 unwanted emails by category including clean
This contrasts with last year’s reported number of 36.3% of all emails being categorized as “unwanted”, showing a slight increase in unwanted emails year over year.
When you consider that we processed 55.6 billion emails in 2024 the number of unwanted emails accounts for roughly 20.5 billion “unwanted” emails sent to businesses over the reporting period.
For a concise breakdown of percentages that make up “unwanted” emails, we classified them as follows:
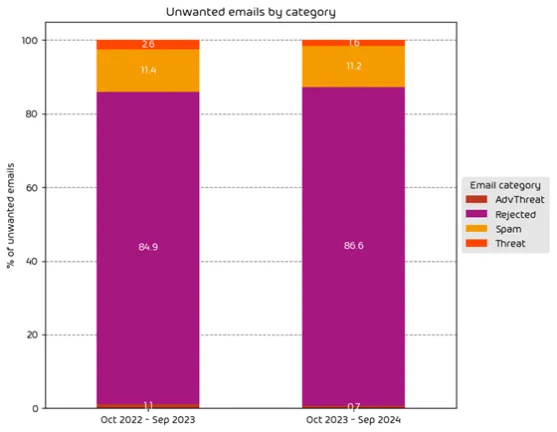
2024 unwanted emails by category
The definitions of each category type are as follows:
| Category | Description |
|---|---|
| Spam | These emails are unwanted and are often promotional or fraudulent. The emails are sent simultaneously to a large number of recipients. |
| Threat | These emails contain harmful content, such as malicious attachments or links, or they are sent to commit crimes like phishing. |
| AdvThreat | Advanced Threat Protection has detected a threat in these emails. The emails are used for illegal purposes and involve sophisticated technical means that can only be fended off using advanced dynamic procedures. |
| Rejected | Our email server rejects these emails directly during the initial connection from the sending email server because of external characteristics, such as the sender’s identity, and the emails are not analyzed further. |
NOTE: To provide a little more detail, the “Rejected” category refers to mail that Hornetsecurity services rejected during the SMTP dialog because of external characteristics, such as the sender’s identity or IP address. If a sender is already identified as compromised, the system does not proceed with further analysis. The SMTP server denies the email transfer right at the initial point of connection based on the negative reputation of the IP and the sender’s identity.
Attack techniques used in email attacks in 2024
In our data analysis of emails from the data period we observed the below breakdown of attack types used in email attacks:
| Attack Technique | Percentage |
|---|---|
| Phishing | 33.3 |
| URL | 22.7 |
| Advanced-Fee Scam | 6.4 |
| Extortion | 2.8 |
| .Exe in Disk Image / Archive | 2.4 |
| Impersonation | 1.8 |
| HTML | 1.7 |
| Maldoc | 0.5 |
| “Other” | 28.4 |
NOTE: In previous years we’ve been able to track the change in occurrence of attack types from year to year. However, due to changes in how we identify malicious items and unwanted emails, there is a subset of occurrences that are marked as “Other”. This category includes various attack methods that do not neatly fit into one of the main categories we’ve displayed in previous years. While we can provide a breakdown of attack types for this data period, comparing this data directly to last year would not yield an accurate representation.
- What our data does show us for this data period is that Phishing remains the number one attack type used in email-based attacks, followed by malicious URLs. The growing popularity of malicious URLs among attackers is largely driven by their use in reverse-proxy credential harvesting attacks, leveraging tools like Evilginx.
Outside of that, Advanced-Fee scams are still quite popular amongst threat-actors followed by extortion in 4th place. Extortion is notable as we continue to see cases where threat-actors will first exfiltrate data prior to putting ransomware in place within a given environment. Should the target refuse to pay (due to recovering from backup) the threat actor will threaten to release the data to the public.
Attachment use and types in attacks
Email attachments continue to be used by threat actors for the delivery of malicious payloads in 2024. Threat actors use attachments to hide malware as well as add an air of authenticity to their malicious communications, depending on the attached file type in use.
Additionally, some rudimentary spam/malware filters may be unable to scan certain file types leading to infection by more complex attacks such as HTML smuggling. In fact, the use of malicious HTML files remains in the number one spot for most used file types used in malicious emails, as shown below.
The breakdown of the file-types used for delivery of malicious payloads over the data period is shown below:
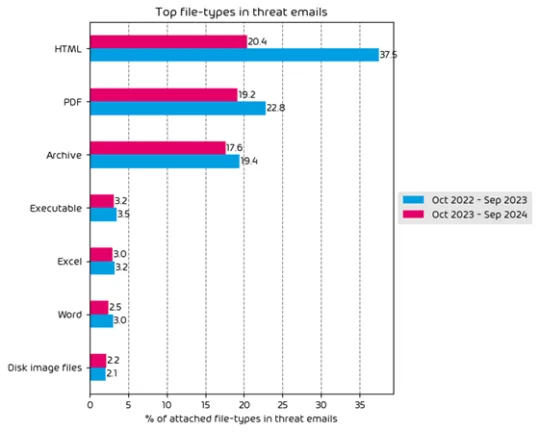
File-types for malicious payloads in 2024
There is a 17.1 percentage point drop in the use of HTML files in 2024 compared to 2023.
PDF file usage saw a 3.6 percentage point decrease in 2024.
Archive files saw a similar trend in a percentage point decrease of 1.8 in 2024.
We observed a near universal decrease in all malicious file types as attackers pivot to other attack styles.
Over the past year, the use of malicious attachments has not been as useful for threat actors as it has in the past. As such we’ve seen a trend where attackers are pivoting to more social engineering with the goal of getting the target to take an action other than open an attachment.
For example, the use of reverse-proxy adversary-in-the-middle toolkits has seen much use during the data period. This is due to the fact that with increasing adoption of Multi-Factor Authentication (MFA), attackers are leveraging token theft more frequently via tools like Evilginx and PyPhisher. It’s easier to procure the authentication token as opposed to dealing with the headache of gaining access to the target’s MFA method.
Stay Ahead of Cyber Threats with Advanced Threat Protection by Hornetsecurity
Nowadays, staying one step ahead of cybercriminals is crucial. Hornetsecurity’s Advanced Threat Protection leverages cutting-edge AI technology to safeguard your emails and data against even the most sophisticated attacks. From ransomware and spear phishing to zero-day threats, our self-learning, AI-based detection mechanisms ensure your business is protected at all times.

Why choose Hornetsecurity’s Advanced Threat Protection?
- Comprehensive Defense: Protect your inbox from ransomware, CEO fraud, and other cyber threats.
- AI-Powered Security: Utilize advanced AI tools to detect and prevent malicious activities.
- Real-Time Alerts: Stay informed with immediate alerts on any potential threats.
- User-Friendly Experience: Enjoy quick setup and seamless access to all features via our intuitive dashboard.
- Powerful Features: Benefit from features like sandboxing, secure links, QR code analysis, and malicious document decryption.
- Don’t wait for a cyber attack to strike—stay proactive with Hornetsecurity’s Advanced Threat Protection.
Request your demo today and secure your business from unwanted email threats!
Conclusion
As email continues to be a significant attack surface, understanding the evolving threat landscape is imperative for maintaining robust cybersecurity. The data from Hornetsecurity’s Security Lab highlights the persistent risks posed by phishing, malicious URLs, and social engineering tactics. While there is a slight increase in unwanted emails, the adaptation of attack methods underscores the need for continuous vigilance and advanced protection strategies.
Businesses must remain proactive, leveraging insights from reports like this to anticipate and mitigate potential threats. By doing so, they can better protect their systems and data, ensuring a secure communication environment for their users.


