

What Are Email Data Leaks and How to Prevent Them
According to our research published in Cyber Security Report, email continues to be the primary communication channel for many organizations, with over 333 billion emails sent and received daily. Based on projections, that figure will increase to almost 400 billion daily by 2026.
This means that more cyber-attacks are being spread via email. While it may seem like a simple thing, we need to make sure we know how to use email properly, what we’re sharing and who we’re sharing it with.
This article is about email leaks and how to prevent them.
What Is Data Leak? Why Do Data Leaks Happen?
A data leak is when sensitive data is exposed to someone(s) not authorized to see it. Data leaks can occur for two reasons: cybersecurity attacks and inadequate security measures.
Sensitive data includes Personal Identifiable Information (PII) and business data such as project plans, financial details, software code, and other similar types of data.
Personal Identifiable Information (PII) is any data that can be used to identify someone such as their first and last name, email address, phone number, passport number, driver’s license, social security number, and other personal information.
Malicious Methods That Cause a Data Leak
Attackers use various malicious methods that cause data leaks. Individuals or groups employ various methods to trick end users into gaining access to their data. Three common methods are phishing attacks, malware attacks, and brute-force attacks.
Phishing mail attacks are one of the most common malicious methods we see nowadays. According to our Cyber Security Report, almost 40% of attacks are delivered via phishing mails. We often see viruses or other types of malwares integrated into different file types, including Word, Excel, PDF, and archives.
Hackers develop sophisticated emails that look like the real thing and trick you into opening malicious links or attachments to gain access to your network. Phishing attacks are used in combination with social engineering to trick people into revealing their sensitive data by impersonating people.
Phishing attacks are carried out via email, SMS, voice and QR code scams.
Malware is a second method attackers use to try to penetrate your network. It is a broader term that covers various malicious software. This includes viruses, trojans, worms, ransomware, spyware, adware, keyloggers and more. According to our Ransomware attacks survey, 1 in 4 (23.9%) IT professionals say their organization has been the victim of a ransomware attack.
The best protection is Endpoint Detection and Response (EDR) on end user devices, strict firewall rules and security solutions that block internal and external malicious activities. You can read more about malware attacks here Malware vs. Viruses: Understanding the Threat Landscape.
In third place is a brute force attack. In such an attack, your username (email address) is loaded into brute force software, which then attempts to guess a password based on various password combinations stored in dictionaries. Dictionaries can be found for free on the Internet. The best practice here is to have a strong password and use multi-factor authentication.
Poor Security Practices That Cause Data Leaks
There are various reasons for data leaks.
First and foremost is a poor security culture. Your credentials are the first layer of attack. Never use weak passwords to protect your online accounts. If you are an IT administrator, you should enforce a password policy that prevents the use of weak passwords. You can read more in the next section.
When you log in with your account on a shared computer in your company or in public, always make sure that you have logged out. If you don’t and someone else, hypothetically a malicious person, gains access to your email, it could lead to a data leak.
If you are staying in a hotel or your favorite cafe, you should be very careful about which Wi-Fi network you use. There are many scenarios where a malicious person will try to eavesdrop on traffic on an open network.
The best thing to do is to set up a mobile hotspot and use the internet via your cell phone. You can also train your users to use a VPN for every connection, although this does carry the risk that a user might forget to use it on an untrusted network.
An inadequate security measure may also be that someone has unintentionally sent an email to the wrong external email address (misdelivery). Even a second of unintentional action can lead to significant problems for us.
This happens when a user accidentally sends sensitive information to the wrong email address. According to Verizon Data Breach Report 2022, there were 715 incidents, 708 with confirmed data disclosure, that compromised personal, medical, financial, and other data.
Double-check to whom you are sending your email.
If you are using a bad password or a single password for more than one account, please change it immediately. Each account should have a different strong password. Now you are probably going to say how to memorize it!? You don’t need to see below.
Other bad practices usually relate to infrastructure and inadequate policies. You can find out more about this in the section “How to prevent data leaks”.
The Dangers of Bad Password Hygiene
Despite cybersecurity experts and companies advocating for a strong password culture, passwords in many organizations continue to be the weakest link. According to the Specops Breached Password Protection list, there are 2 billion breached passwords, and that number is increasing daily.
It is the responsibility of IT teams to enforce password policies in companies. This primarily includes the use of complex passwords with lower and upper-case letters, numbers and special characters.
Different security solution providers give different recommendations on the number of characters a password should have. The general rule of thumb is that more characters are better. Do not use less than 12 characters.
In the past we often enforced frequent password changes (every 30 days was popular). This has proven to be counterproductive, and both NIST in the US and GHCQ in the UK now recommend not to enforce frequent changes.
This just leads to people picking easier passwords and attaching the number or the name of the month to the end of their passwords for example.
You should also introduce a password history policy to prevent the reuse of old passwords. According to an Online Security Survey conducted by Google, 65% of people reuse their passwords. This is a major security issue.
In addition, you can introduce other password policies such as lockout policies, disabling accounts that are not being used, introducing multi-factor authentication (MFA), assessing password strength, monitoring account access, introducing SSO and others.
The bottom line is that today, just using a username and password for identifying a user isn’t adequate, wherever possible you must use strong authentication such as MFA, including phishing resistant MFA such as FIDO 2 hardware keys, or biometrics such as Windows Hello.
These measures stop 98%+ of all identity-based attacks.
One of the most common mistakes of poor password hygiene is sharing login credentials via email. Imagine if someone were to gain access to your email and find your password? This would mean that a malicious person would be able to compromise your integrity and your data.
Implement Password Managers
Don’t write down your password on sticky notes, notes or anywhere else. It’s best to use a password manager and store your passwords in secure and encrypted password vaults. Whenever you need your password for a service or device, log in to your password manager, copy it and then enter it.
Password Managers also provides you with extensions for your favorite browsers that allow you to retrieve your password when you need to log into your account.
This practice benefits users at all levels, from end users to IT administrators who manage many different systems.
What Should I Do if I Find My Address in an Email Leak?
If you find your address in an email leak, you should immediately change your password. A new password should follow the policy introduced in the previous section.
Use Password Managers to store your password, don’t store it written or printed on paper, stored in .txt or any other files on your machine, or shared via email. Password Managers are designed to do it most securely.
In case of email leaks that happen in organizations, you should inform relevant stakeholders and check if there were any suspicious activities done on affected services.
Note: Do not ignore security breach notifications, ignoring would put your account and data at risk.
How can I know if my account was leaked?
According to haveibeenpwned, as of November 2023, there are over 12 billion accounts leaked. If you want to check if your email or account was leaked, navigate to https://haveibeenpwned.com, enter your email address, and click Pwned?
You can also subscribe (for free) to get notified when future pwnage occurs and your account is compromised, there are also options for organizations to monitor their entire email domain, instead of just individual accounts
How To Prevent Data Leakage
From an IT management point of view, you should introduce access control and define who is allowed to do what. One of the most important measures is to introduce access control with minimum authorizations.
Your data should be encrypted regardless of where it is stored, both in transit and in storage. Even if a malicious person gains access to the data, they cannot read it.
Security is a shared responsibility. Make sure that you implement strong security protection on your network and endpoints and that your employees are trained in handling the data.
In addition, you should ensure continuous monitoring and logging of all activities that take place internally or externally on your services.
Please note that data leaks are not a one-off event, but an ongoing process that requires strong technology and employee awareness.
Many websites or client–server communications do not use TLS (SSL) certificates. This means that the communication between you and your server is in plain text and can be intercepted and read by a criminal.
Make sure that your website uses certificates, that communication is encrypted and that you renew them on time. Better yet, automate the process using a service like letsencrypt which not only ensures your certificates are renewed on time, but also offers free certificates.
Make sure your infrastructure is always up to date at the physical and application level and patched with the latest updates. If our systems are not patched with the latest security updates, this poses a major security risk that can be exploited by attackers to gain access to our network.
To maintain security measures, you should apply compliance regulations and industry standards to prevent data breaches. Some of the factors that can lead to a data leak are shadow IT, poor data processing practices, lack of encryption, poor BYOD (Bring Your Own Device) practices, inadequate employee training and others.
How Hornetsecurity Can Help You Stay Protected Against Data Leaks
According to the World Economic Forum – The Global Risks Report 2022, 95% of all cyber security breaches are caused by human error. Malicious people (read hackers) try to exploit human psychology using phishing and social engineering.
To prevent it, organizations need to provide continuous training to employees on how to use technology and prevent data leaks.
That is where the Hornetsecurity Security Awareness Service comes into play. Security Awareness Services provides fully automated awareness benchmarking, spear-phishing simulation, and E-Training to sensitize and protect employees against cyber threats. Practically speaking, you can train and then challenge your employees by simulating sophisticated email attacks.
Service Awareness Service provides ESI (Employee Security Index) that continuously measures and compares employee security behavior across the organization and offers individual training needs.
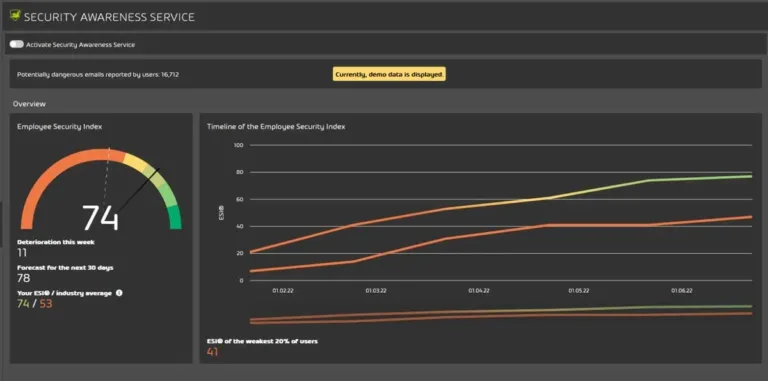
Security Awareness Service also provides an e-learning hub for employees where they learn security content on how to handle phishing attacks in multiple languages.
That is not all.
Hornetsecurity provides several solutions that help you strengthen your security and prevent data leakage including fully automated, secure, and effective email encryption, the cloud-based corporate email platform with integrated spam and malware protection, email archiving service to ensure email data integrity & compliance for M365 and other email servers, powerful spam filtering and malware protection to stay ahead of cybercriminals and more.
You can read full insights into different Hornetsecurity solutions that help you stay safe. You can read more here Email Cloud Security Services from Hornetsecurity.
Remember, the best way to protect against malicious methods is to have a proper understanding and implementation of IT Security.
To properly protect your cyber environment, use Hornetsecurity Security Awareness Service, and Advanced Threat Protection to secure your critical data.
We work hard perpetually to give our customers confidence in their Spam and malware Protection, Email Encryption, and Email Archiving strategies.
To keep up to date with the latest articles and practices, pay a visit to our Hornetsecurity blog now.
Conclusion
Data leaks are a constant challenge that occurs in many organizations. There are two reasons for this. The first is when users accidentally share data by sending sensitive emails to the wrong email address or forgetting the USB stick with the data in a public café. The second is when malicious people attack our infrastructure with malware.
There is a solution for both cases. IT teams should implement strict security mechanisms from the physical to the application level, strict access control and good password policies and enforce MFA for all user accounts
Security is a shared responsibility. Employees should be trained in the proper handling of emails, passwords and anything that could put data at risk.
Hornetsecurity offers an e-training and security awareness service platform that allows you to educate and challenge your employees by exposing them to fake phishing attacks that look like real attacks.
In this article you learned all about data leaks and how to prevent them.
FAQ
When sensitive data is leaked, it can have various consequences, such as privacy issues, financial losses, reduced customer satisfaction and business disruption. If our data is exposed, especially if we are vendors, it has a negative impact on our reputation. Any data leak should be taken seriously, and we must take all preventive measures to stop it.
It is considered bad and risky to pass on your e-mails. Malicious people can use them to target you with phishing and social engineering attacks. To protect your email, you should use or enforce a strong password and enable multi-factor authentication.
If your password has been leaked, it means you are in trouble. A malicious person could access all of your online services that use this password and thus obtain and expose your data. If you use the same password for multiple services, a malicious person could try to access all services and compromise your reputation and the integrity of your data.
Hackers or hacker groups are looking for data with which they can blackmail you, demand money or pass on your data to third parties who could be of use to them.
