
Crypto Mining: Definition and Function Explained
What danger does Crypto Mining pose to companies and how can you protect yourself against them?
With the establishment of cryptocurrency, the era of a new means of payment has been ushered Crypto Mining in. To better understand the miners’ gold rush, we have summarized the most important facts on this page.
Table of Contents
How Does Crypto currency work?
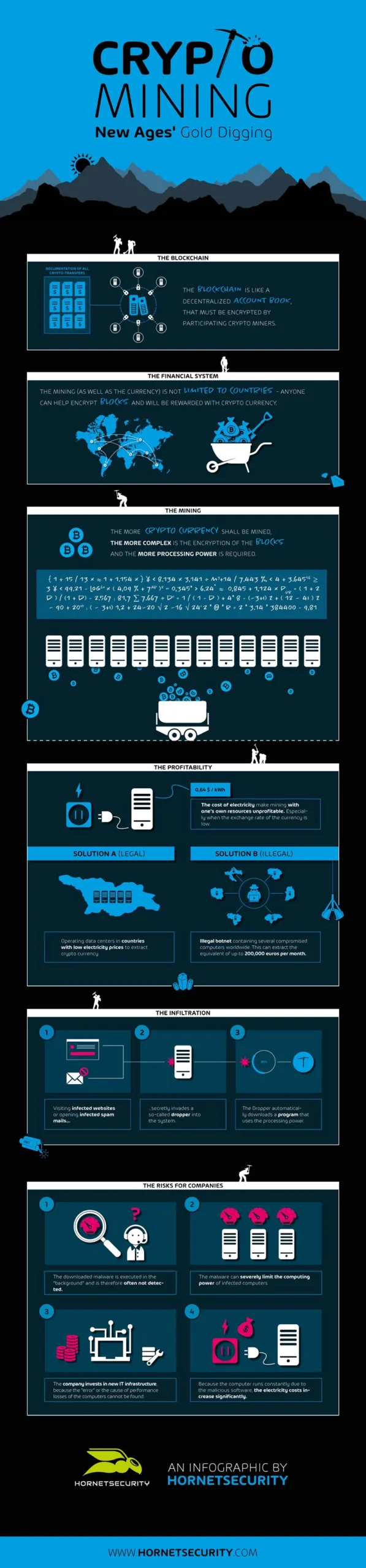
We started with Bitcoin, which was first described in 2008 by the Japanese Satoshi Nakamoto in the Bitcoin white paper. His idea: The establishment of a digital currency. This should be organized decentrally, i.e. neither governments nor banks should administer it. The maximum number of Bitcoins should be limited to a total of 21 million, in order to exclude inflation from the outset. Unlike central banks, however, Bitcoin units are not printed like banknotes, for example, but can only be generated digitally by computing power.
The basis for this is the so-called “block chain“. This is because in Crypto Mining or Bitcoin Mining, each individual transaction is grouped into “blocks”. These are then lined up in a linear sequence and linked together via a decentralized peer-to-peer network. All blocks have so-called “hash values“, which are a kind of check number for the transactions made. The check number in turn contains the individual hash values of the current transaction as well as the hash values of the respective previous transaction. For their generation, a conventional computer can be used, which performs a cryptographic function, also called “hash function” (SHA256).
Thanks to this procedure, manipulation of the transactions is impossible, since a subsequent change within the chain would not only stand out, but is not even mathematically possible. If only one value were to be manipulated, the subsequent value would also deviate from the actual sequence.
Difficulties with the Generation of Cryptocurrencies
Simply explained, there are two different possibilities to mine cryptocurrency. These are private crypto mining from home and crypto mining via the cloud. The two possibilities will be examined in more detail below:
Private Bitcoin Mining
The foundation stone for every type of crypto mining is the so-called eWallet, which is used to store the cryptocurrencies generated during mining (e.g. Bitcoins, Moneros and Co.). In addition, private Bitcoin Mining requires a special program that can execute the hash function for mining. This can be installed and set up quite easily by any PC owner.
Although it is still possible to run Crypto Mining from home with the CPU of your own computer, it is not recommended nowadays for economic reasons. One reason for this is that there are now chips specially developed for crypto mining, known as “ASIC” (Application Specific Integrated Circuit), which can mine cryptocurrencies up to one hundred times more efficiently and seven times faster. But even this is not always profitable compared to crypto mining via the cloud.
Crypto Mining vie the Cloud
If you want to save yourself the trouble of operating Crypto Mining from home, you can rent hash services from a cloud mining provider. Meanwhile there are countless different providers, some of which operate entire mining farms. The contracts can be concluded for different crypto currencies via the website of the respective provider. The costs of the contracts depend on the rented service. Thus the providers remain independent of the value of the cryptocurrencies.
Legal and Illegal Crypto Mining – What are the differences?
Crypto Mining is an extremely complex, resource-intensive – and therefore expensive – process. While in the early days of Bitcoin and Co. it was sufficient to use your own PC to mine the coveted online money, the situation today is different. Since the value of the cryptocurrency decreases with the increasing amount of units generated, a so-called “halving” takes place at regular intervals. This ensures that from a certain point in time it is twice as time-consuming to generate a unit of a crypto currency. This measure is necessary because otherwise inflation would occur. Conversely, this means that more and more computing power is required to generate the unit of a cryptocurrency.
The power consumption and the wear and tear on the hardware are increasing rapidly. Digging with one’s own computer simply becomes unprofitable. Resourceful Crypto Miners soon began looking for new ways to mine crypto currencies more profitably. Completely new possibilities quickly established themselves: One is the mining of cryptocurrencies in countries with very low energy prices, such as Iceland, Venezuela or Georgia. Entire industries have already developed in these countries, some of which are now a problem for the stability of the national power supply. Iceland has already experienced an energy shortage due to the rapid increase in crypto mining activities. The consequences: A significant shortage of the sought after commodity and increasingly expensive production.
An almost free, but also illegal method is the generation of cryptocurrencies with the help of a botnet. The aim here is to make as many computers as possible part of such a network and have them mine crypto currencies in a network. The generated units are then credited to the cybercriminals’ eWallet. To do this, they smuggle malware onto their victims’ computers. How the criminal miners succeed in this is described below.
Illegal Crypto Mining – How cyber criminals tap into your computer
Basically, a distinction must be made between two types of illegal crypto mining:
Crypto Mining using JavaScript Commands
The most widespread method is the use of the crypto mining program Coinhive, which is classified as a “potentially harmful program” by most antivirus programs. Since it is based on JavaScript, it can be easily installed on web pages and is easily downloaded by most browsers. The legal situation, however, is anything but clear. IT security expert Brian Krebs recently called the program “one of the greatest threats to web users”.
And indeed, the program’s approach is extremely perfidious. Coinhive-infected websites force their visitors’ devices to dig up crypto-currencies – usually without the victim noticing or obtaining prior consent. Some of them even use the full CPU power, such as the Crypto Mining program that was included on the website of Portuguese football star Cristiano Ronaldo.
This method has a decisive disadvantage for Coinhive users: Cryptocurrencies are only mined as long as someone is actually actively on the website. If they leave the site, the crypto mining process is aborted.

Crypto Mining via Malware
Crypto mining using malware, also called cryptojacking, is a completely different matter. This method uses malware specially designed for mining cryptocurrencies. The cybercriminals use different ways to smuggle it onto the computers of their victims.
The most popular method of distribution is via infected websites. But pirated software is also suitable as a hiding place for a crypto mining dropper. If a user calls up an infected download website, the malware is loaded onto the computer unnoticed via a drive-by download and begins to dig up a selected crypto currency for the hackers. Since the maximum computing power of the devices is to be used to the full, the cyber criminals must proceed with caution in order not to be discovered while digging. Because if the device is always running at 100 percent computing power, it can hardly be operated by its owner. In most cases, the user will then take countermeasures.
As a result, Crypto Mining Malware usually uses only about two thirds of the computing power. In some cases, the malware is even programmed to detect the start of an application that uses resources and to throttle the malware’s activities accordingly. Crypto Mining Malware has even been detected that is able to bypass antivirus programs. However, many independently infected devices do not yet give cybercriminals much use. The important thing is that they can bundle their power to mine crypto currency. A bot network is the ideal tool for this. Some of these networks comprise several thousand computers, and the profits that cybercriminals make are correspondingly high.
How do I protect myself from illegal crypto mining?
First of all: There is no “that” protection against illegal crypto mining, but rather a combination of different security solutions to combat unwanted mining.
On the one hand, it is important to understand how cyber criminals proceed in illegal crypto mining and what tools they use. The right security awareness can lay the foundation for effective prevention.
As a supplement, an anti-virus program should be installed on the computer, which is always kept up to date – this naturally also applies to all other programs and the operating system. If you want to download software from the Internet, you should only do this via trustworthy sources such as heise.de. Renowned download portals also offer software for download that wants to install additional software during the installation process. It cannot be ruled out that this may contain additional malware such as crypto mining droppers.
Furthermore, spam e-mails may also contain links that lead to websites contaminated with Crypto Mining Droppers. As it can be difficult to distinguish well-done spam e-mails from normal e-mails, it is recommended that companies in particular use a managed spam filter service. Increased attention is also advised when surfing the web. Since dubious, malware-infected pages are of course only rarely recognized as such, the use of a web filter is also recommended. This reliably warns the user of potentially harmful content before calling up the page. This provides protection not only against Crypto Mining Malware but also against all other harmful content.
Visit our knowledge base
Did you like our contribution from the knowledge database on Crypto Mining? Then you can access the overview page of our knowledge database here. There you can learn more about topics such as Phishing, Brute Force Attacks, GoBD, Cyber Kill Chain, Computer Virus and Ransomware.
