

How to Avoid an Email Security Breach
Email is still the most important communication channel. More than 300 billion e-mails are sent and received every day. According to forecasts, this figure will increase to almost 400 billion a day by 2026.
Hackers know this and are constantly targeting companies, infecting them via email with various types of malware or phishing attacks. But this only happens when companies have poor security hygiene and fail to provide ongoing employee training.
As an example, in 2019, healthcare organization NHS Highland inadvertently disclosed the health records of 40 HIV-positive people by sending an email via CC rather than BCC. This was considered an email security breach.
This article is about email security breaches and how to avoid them using best practices and Hornetsecurity’s email security services.
We all want to stay ahead of a malicious email leading to a compromised business. Don’t we!?
Understanding Email Data Breaches and the Importance of Email Security
A data breach is data loss or data compromise due to inadequate security measures or human error.
Malicious actors are targeting our infrastructure using various techniques such as malware, phishing, and social engineering. In most cases, these attacks are carried out via email. The hackers try to trick us into opening links or attachments that give them access to our infrastructure and data.
Even if we have the most advanced security measures and systems in place, this is of no use if our employees are not trained in the correct handling of devices, emails, and data.
The first target of most cyber attacks is people. Attackers use our human psychology against us, our willingness to help others or our lack of understanding of the risks involved in email attacks.
The introduction of strong email security measures and employee training reduces the risk of being hacked.
Notable Examples of Massive Email Data Breaches
There have been several data breaches in the last decade. We will not go into all of them, but we will mention a few major data breaches.
In August 2013, Yahoo was attacked by a hacker group. Over 3 billion email accounts were compromised.
In 2018, hackers gained unauthorized access to Aadhar, the largest ID database in India. Over 1.1 billion Indian citizens were affected by this data breach, including their data such as names, addresses, photos, phone numbers, emails, and biometric data.
In July 2019, hackers gained access to over 100 million accounts hosted by Capital One. The hackers stole credit information affecting around 100 million people in the US and around 6 million accounts in Canada.
In June 2021, LinkedIn discovered that 700 million of its user accounts had been exposed to the dark web. This was the largest data breach the company had experienced.
There are dozens of other data breaches that can be traced back to inadequate security measures.
Exploring Vulnerabilities Stemming from Weak Email Security
Weak email security can expose company data and vulnerabilities. Weak email security is related to weak passwords, lack of multi-factor authentication, lack of security measures against phishing and spam, lack of email encryption, lack of email security policies, lack of ongoing training, and others.
Even failing one of these can damage the integrity and reputation of a company and put it in financial difficulties.
Where there is weak email security, there is plenty of scope for attacks and email security breaches. Attackers can easily penetrate our network and exploit vulnerabilities from the physical to the application layer to attack our unpatched systems, unencrypted storage, unpatched systems, and others.
To minimize the risk, companies should invest in robust email security measures.
Recognizing Signs of a Hacked Email Account
If you suspect that your email account has been hacked, there are several signs you should look out for. Please note that these signs, especially if they are suspicious activity (they could be you), are not always proof that your account has been hacked, but they should trigger an alert to check it out.
There are two possible scenarios. Your account has been hacked and you can no longer use it, or your account has been hacked and you can still use it.
In the first case, hackers have compromised your email account and data and changed the password.
You have tried several times to re-enter your web or email client password, but it does not work. If you have been authenticated in the Outlook client application, you are prompted to re-enter your password. You have probably been hacked.
In the second case, the hackers have compromised your email account but have not changed your password. If you have configured this, you should receive a notification about unusual or suspicious activity in your email account.
Email accounts have a security service that sends emails directly to you or your alternate email address when suspicious activity is detected.
These activities may include notifications of unauthorized access from unusual IP locations or devices, password change notifications, unexpected password reset emails, changes to account information, and unknown devices connected to your email account.
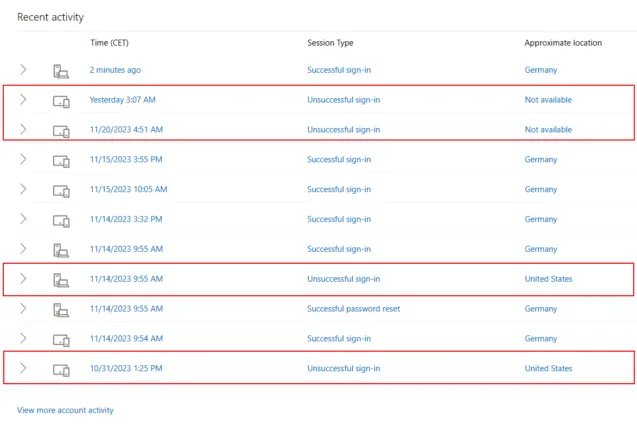
You should always pay attention to these notifications, even if you think it’s not a sign of malicious activity. For example, if you were logged into your email in Germany, then traveled to the US and continue to use your email, your email service will trigger a notification of a new sign-in activity from a different country.
In this example, we see that someone tried to log into my email account from the US and an unknown location, and it wasn’t me.
Additionally, if your internal or external colleagues are receiving spam or phishing emails from your account that you did not send, your account is likely compromised.
Note that sometimes an email may appear to be from you, when in fact it was sent from a different email address and merely uses your email addresses as “cover” to make it more likely to slip through defenses.
Check if there are any suspicious emails in the “Sent” folder or if there are any forwarding rules in place to forward emails from your account to a third party’s email address.
Steps to Take If Your Email Security Has Been Compromised
If you are an IT Administrator and you notice in the breach list that some of the emails within your organization are breached, you need to take immediate security measures and inform affected parties.
First and foremost, change the email password and implement (MFA) multi-factor authentication. If you are an end-user and find that you can no longer log in, report the incident to your IT team immediately.
Check your account settings to see if they have been changed. Since many apps are registered to a specific device or you, check the apps and devices associated with your email account. If you notice any unknown devices, block them immediately.
Also, check account activity and see where you have logged in or tried to log in without authorization.
Malicious people could be sending emails to your contact list. You should check your folders for sent, received, and deleted emails. Also make sure that your contact list is informed, as they may have received emails from you that originate from malicious people.
Scan your computer and network for malware and viruses.
Once you have found the root cause and taken the measures mentioned, you should find out what caused it, document it, and strengthen your security measures to prevent it from happening again.
How can you do this? Read the section below on Hornetsecurity.
Strategies for Organizations to Mitigate Simple Email Mistakes
One of the most common email errors is incorrect delivery. That is, when you accidentally send a confidential email with or without attachment to the wrong external email contact.
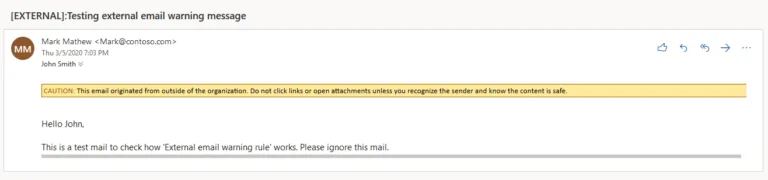
One of the ways to alert employees when the company sends email notifications is through external email notifications. Microsoft 365, for example, offers you the option of activating external email alerts. If you send an email to an address outside your company, you can see the warning as a precautionary measure.
Another example of incorrect delivery is the improper use of CC and BCC email fields. In 2019, representatives from the healthcare organization NHS Highland sent emails to nearly 40 HIV-positive people, publicly exposing them and breaching confidentiality.
What did they do to publicly expose them? They sent an invitation to a support group run by a health clinic, using the CC and not the BCC (Blind Carbon Copy) email field. For the sake of sharing, with CC all recipients are visible to everyone, whereas those who are BCC’ed are not visible to anyone.
Another mistake is not recognizing spam. Spam is an unsolicited advertising message that. Phishing emails on the other hand are malicious emails, either with links to malware or some other dangerous site, or malicious attachments. Users should be trained to recognize these and report them immediately to the IT department.
How can you mitigate these simple email mistakes? By providing continuous security awareness training and challenging users’ actions.
Additionally, use email filtering and security detection to block malware, spam, and phishing attacks before they land in your user’s inboxes.
Reducing the Risk of Email Data Breaches: Best Practices
Security is a shared responsibility. It is the organization’s responsibility to implement security measures and training on security, and it is the end users’ responsibility to follow them.
First and foremost, make sure you have a strong password culture. That means enforcing various password policies within your organization. These policies include password complexity, password length, minimum and maximum password age, password history, password lockout, and others.
For example, the password’s complexity determines which characters should be included in it, while the length determines how long it should be. If you apply these two policies to your email accounts, you can get a password with at least 12 characters, including upper and lower case letters, numbers, and symbols.
As far as password guidelines are concerned, you should never use the same password for multiple accounts. If one is hacked, so can all the others. Also, never use personal information in your password.
Using a strong password is not enough. You should implement MFA (Multi-Factor Authentication). With MFA, you must confirm your identity via SMS, app, or biometric data. If a hacker were to hack your password, they would be unable to successfully log in if they do not have access to your phone. MFA is a must. Not an option.
Hackers use social engineering and phishing to trick you and gain access to your computers. How can you fight them? With solutions like the Hornetsecurity Security Awareness Service, you can also simulate phishing attacks and create sophisticated phishing emails that train users to spot suspicious emails. With this service, you can target everyone from entry-level to C-level.
Phishing attacks will still come after the training. You should implement email security measures that recognize and block phishing attacks in time.
You can find out more about preventive phishing measures in the section Protect your brand with Hornetsecurity: The role of email security.
There are other practices that are a variation of what we mentioned above.
Protect Your Brand with Hornetsecurity: The Role of Email Security
Hornetsecurity offers you a range of tools to strengthen your email security and mitigate email data breaches. These include advanced threat protection, spam and malware protection, and email encryption.
Advanced Threat Protection
Advanced Threat Protection protects your organization from advanced cyber security attacks and threats such as ransomware, phishing, and more. This is very important protection as malicious individuals and groups target organizations with malware such as Emotet, Tribot, GandCrab, and others. The easiest way to send them is via email.
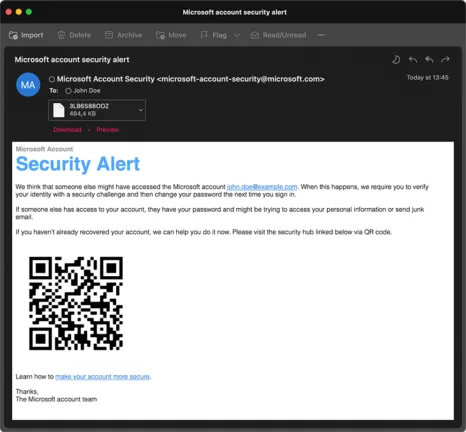
We are trying to make our lives easier by providing everyone with a QR code to download or access a specific website. It’s easier to scan it than to type it in. Isn’t it? Very often hackers put links that direct you to a malicious website to download or simply access a link.
Advanced Threat Protection offers a QR Code Analyzer that analyzes QR codes and checks if they are malicious, in which case the email is blocked accordingly.
Advanced Threat Protection protects you against blended attacks that are combined into a single email attack. Blended attacks include different types of malware such as viruses, spyware, spam, and phishing.
Hornetsecurity uses various technologies to protect you from email attacks, including sandboxing, freezing, safe links, URL scanning, real-time alerting, and ex-post alerting.
The sandbox engine scans the attachment in an isolated environment and checks for malicious activity. If the document is malicious, the file is quarantined, and the IT Security team is notified. If a file cannot be classified as malicious, but seems suspicious, Hornetsecurity freezes it for a short period.
Advanced Threat Detection also helps you to scan links before you open them. If you receive attacks such as PDF or Word documents and they contain links, the URL scanning engine can scan them without compromising the integrity of the document.
When an attack occurs, Advanced Threat Protection sends a real-time alert and informs you accordingly. It also supports ex-post alerts to inform you about emails that have already been delivered and are subsequently classified as malicious. It’ll even reach into user’s mailboxes and delete malicious emails that have already been delivered.
Email Security
Hornetsecurity email security offers you a powerful spam filter and protection against malware. According to our research, 50% of the world’s email traffic is spam. Email Security offers the highest detection rate on the market, with 99.9% guaranteed spam and virus detection.
It protects you from DDoS attacks and phishing emails.
It also supports informal filtering, data traffic encryption, link tracking, phishing filters, automatic virus signature updates, outbound filtering, bounce management, dynamic virus outbreak detection, and multi-level spam detection.
In 2023, Hornetsecurity processed in excess of 45 billion emails which provides a unique opportunity to identify emerging threats and critical vulnerabilities, reveal important trends and can make informed projections for the future of Microsoft 365 security threats, enabling businesses to act accordingly. Read more in our Cyber Security Report.
Hornetsecurity spam filtering and malware protection can be integrated into the email management system. Ask about Spam Filtering and Malware Protection now.
Email Encryption
Email encryption enables the encrypted exchange of emails. This is extremely helpful when exchanging sensitive data and attachments. If a hacker intercepts them, they can read them.
It supports all standard encryption technologies including S/MIME, PGP and TLS. It takes minimal effort to manage encryption, user certificates and encryption policies.
Email encryption includes the following features: Testing option for encryption suitability, automatic digital signing & encryption of outgoing emails via S/MIME and PGP, automatic certificate management & key storage, individual setup and definition of encryption policies, personal email certificates, confidential communication via Websafe, and others.
You can read more here Encrypted email – secure email with PGP, S/MIME, TLS Email Encryption.
You can also opt for email compliance and productivity tools for email archiving, signatures and disclaimers, and continuity services.
Security Awareness Service
According to the World Economic Forum, 95% of all cyber security incidents are caused by human error. One of the types of human error is clicking on suspicious links and attachments in phishing emails. Hornetsecurity has developed a solution that simulates realistic phishing emails and is aimed at everyone from entry-level to C-level.
The solution is called Security Awareness Service. It is a fully automated awareness benchmarking, spear phishing simulation, and e-training to raise awareness and protect employees from cyber threats.
It offers an ESI (Employee Security Index) that continuously measures and compares the security behavior of employees throughout the company. Based on the target group in your company and their ESI index, you can develop a customized training course that is tailored to their needs.
Weekly, monthly, or however you like, you can trigger phishing emails and test your employees’ phishing detection skills.
This way your network stays safe.
To properly protect your cyber environment, use Hornetsecurity Advanced Threat Protection to secure your critical data.
We work hard perpetually to give our customers confidence in their Spam & Malware Protection, Email Encryption, and Email Archiving strategies.
To keep up to date with the latest articles and practices, pay a visit to our Hornetsecurity blog now.
Conclusion
Email security breaches let malicious individuals or groups access your company data. This happens due to inadequate security measures and a lack of security awareness.
Hackers attack companies through emails by using social engineering and phishing attacks. The idea behind these two attacks is to trick people into opening malicious links and attachments in email in order to gain access to their data. It is one of the most common malicious methods.
Another way for hackers to gain access to emails is if organizations or companies use weak email security. This indicates weak passwords, lack of multi-factor authentication and inadequate email security software.
Security is a shared responsibility between IT teams and employees. IT teams should implement strong email security measures and enforce policies, and employees should follow them.
This article covered email security breaches, how they occur, and what users and organizations can do to prevent them. It also demonstrates the power of Hornetsecurity’s email security solution.
